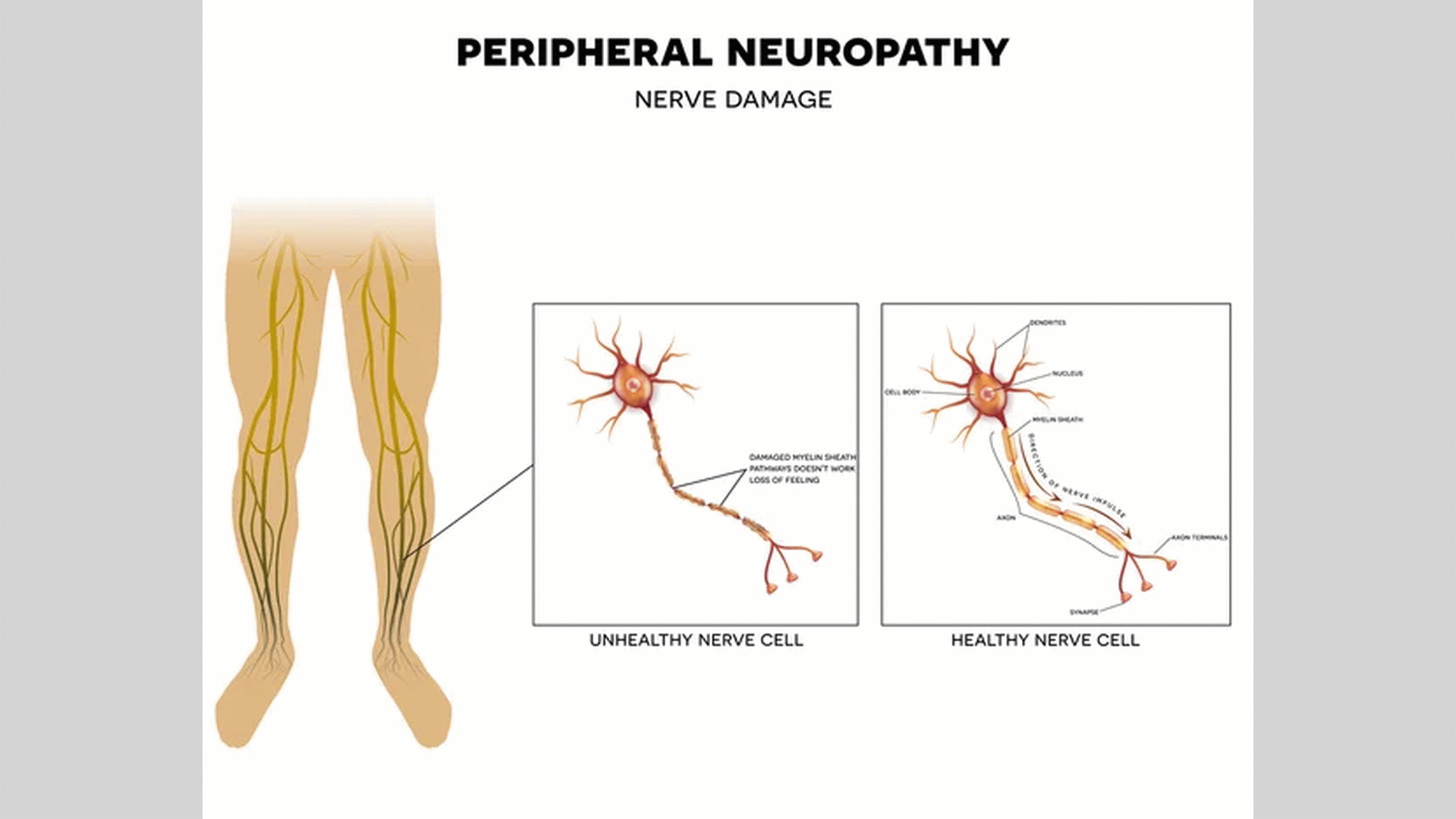
Neuropathy occurs due to damage to the myelin, a fatty layer of protection covering the nerves. This condition may lead to unusual sensations, discomfort, or pain. Typically, medication is used to treat unpleasant sensations. Addressing the underlying condition can sometimes halt the progression of neuropathy.
Neuropathy can impact various nerves throughout the body, often following a specific pattern of nerve involvement. There are several types of neuropathy, including peripheral neuropathy, which affects the nerves controlling limb movement and sensation. This type is commonly associated with age-related diseases like Parkinson’s disease, increasing the risk of peripheral neuropathy with age.
Autonomic neuropathy affects involuntary nerves that regulate organ function, such as intestinal movement, blood pressure, heart rate, heart contraction strength, and urination. It is often linked to diabetes and systemic illnesses like kidney failure.
Proximal neuropathy affects nerves closer to the body, such as those in the upper arm, shoulder, and thighs. It is less common than other types and can occur independently or alongside peripheral neuropathy. Severe peripheral neuropathy may involve proximal nerves as it advances, typically affecting one side of the body more than the other.
Causes of proximal neuropathy include cancer and inflammatory diseases like Guillain-Barré syndrome. Focal neuropathy, another common type, encompasses conditions like ulnar neuropathy and carpal tunnel syndrome, resulting from nerve compression due to pressure, often from prolonged positions or repetitive limb use causing inflammation.
Role of homeopathy in neuropathy
In treating neuropathy, homeopathy aims to address the underlying cause of the problem, such as infections, diseases, tumors, or injuries, instead of just alleviating the symptoms. While doing so, it also addresses the symptoms such as tingling sensation and numbness.
Seven homeopathic medicines for neuropathy
Hypericum perforatum
Common name: St. John’s Wort
Hypericum perforatum is indicated for neuropathy with shooting pains, especially after injuries or surgeries. The affected area feels painful, raw, or bruised in injured areas. There is presence of numbness with tingling sensations and neuralgic pains that extend to other parts of the body.
Arsenicum album
Common name: Trioxides of arsenic
Arsenic album can be prescribed for burning pains in the legs and hands, particularly in the soles of feet and tips of fingers, due to neuropathy. Individuals might be restless and anxious, especially at night. Numbness and weakness are present at the affected site. The intensity of symptoms is higher at night, leading to sleep disturbances.
Agaricus muscarius
Common name: Toadstool
Agaricus muscarius for neuropathy is recommended for those having tingling, crawling, or itching sensations in the hands and feet. Numbness with jerking or twitching of muscles, especially in the fingers and toes, is present with a feeling of coldness or burning in the affected areas due to neuropathy.
Plumbum metallicum
Common name: Lead
Plumbum metallicum is indicated in neuropathy with muscle weakness and wasting, especially in the lower limbs. There are cramping pains, with a sensation of tightness or constriction and numbness with paralysis of the limbs.
Phosphoricum acidum
Common name: Phosphoric acid
Phosphoricum acidum is prescribed for those with nerve weakness and exhaustion from mental or physical exertion. The person may complain of numbness and tingling, especially after prolonged stress or grief. There is memory loss and mental fatigue, with a sensation of emptiness.
Nux vomica
Common name: Poison nut
Nux vomica is recommended for individuals with shooting pains, cramps, and numbness aggravated by cold and relieved by warmth. Numbness and tingling in the limbs, especially in the morning or after meals is indicative of this remedy. There is sensitivity to noise, light, and odors, with irritability and impatience, along with digestive disturbances, such as constipation and indigestion.
Kalium phosphoricum
Common name: Phosphate of potassium
Kali. phos. is recommended for neuropathy caused by nerve damage due to overwork, stress, or loss of fluids. There is weakness and trembling of limbs, with a sensation of heaviness, numbness, and tingling, especially after mental or physical strain. Individuals may also have difficulty concentrating, forgetfulness, and mental fatigue.
Causative factors of neuropathy
- Alcohol abuse.
- Facial nerve conditions like Bell’s palsy.
- HIV or AIDS.
- Central nervous system disorders like stroke, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis.
- Complex regional pain syndrome.
- Infections like shingles.
- Chemotherapy drugs.
- Radiation therapy.
- Amputations which can cause phantom limb pain.
- Spinal nerve compression or inflammation due to disc bulge or disc prolapse.
- Trauma or surgeries with resulting nerve damage.
- Tumors that press on nerves.
Symptoms of neuropathy
Spontaneous pain
Pain that happens for no apparent reason. This includes a burning, stabbing, electric shock-like pain, tingling, numbness, or a feeling of ‘pins and needles’.
Increased sensitivity
Increased sensitivity occurs when normally painless stimuli like cold, pressure, or brushing against your skin causes you to feel pain. It’s an extreme sensitivity to touch.
Increased sensitivity to pain
Increased sensitivity to pain happens when normally painful stimuli like heat or pinpricks cause an extreme or increased pain sensation. For example, the pinprick hurts more than it should.
Decreased sensitivity
Decreased sensitivity occurs when a normally painful stimulus results in a decreased pain response. For example, the pinprick should hurt, but it doesn’t.
Various sensation
Any unexpected sensations that feel strange, unpleasant, or painful. The sensation is like something crawling or moving on the affected part.
Difficulty sleeping
There may be emotional stress due to disturbed sleep and pain.
Treatment for neuropathy
Neuropathy occurs due to damage to the myelin, a fatty layer of protection covering the nerves, or nerve damage, which may occur in severe cases. The body can naturally renew myelin, so sometimes, the loss of myelin heals if the damage stops happening. Usually, neuropathy treatments are focused on preventing nerve and myelin damage by controlling the cause of it. Symptomatic treatment gives relief from discomfort or pain.
Treatments for neuropathy may include blood sugar control to prevent the progression of diabetic neuropathy, limiting alcohol to prevent the progression of alcohol-associated neuropathy, and using anti-inflammatory medicines to reduce nerve damage when neuropathy is caused by any systemic inflammatory disease.
The treatment for neuropathy caused by pressure, such as carpal tunnel syndrome, includes resting, wearing splints, and going to physical therapy. Focal neuropathy improves with treatment, often with complete resolution of symptoms. Surgery may be suggested to treat compression, such as with ulnar neuropathy or carpal tunnel syndrome.
There is no standard treatment that can specifically heal a nerve. Physical therapy can sometimes improve motor function by learning to adapt and maximize your abilities. Medications that are often used to control neuropathic pain may include antiepileptic and antidepressant drugs. These medications affect nerve activity that can subdue the pain.
Diet and lifestyle modification in neuropathy
- Consume fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats for a balanced nutritional intake.
- Incorporate sources of vitamins B12, B6, and E and omega-3 fatty acids into your diet.
- Limit consumption of sugary snacks and processed foods to maintain a healthy diet.
- Control alcohol consumption to support nerve health and overall well-being.
- Indulge in walking, swimming, or cycling for optimal fitness.
- Enhance flexibility and alleviate muscle tension through stretching exercises.
- Adhere to a diet suitable for people with diabetes and monitor blood glucose levels consistently.
- Inspect feet daily, maintain cleanliness, wear well-fitting shoes, and avoid walking barefoot.
- Incorporate meditation, deep breathing, yoga, or progressive muscle relaxation into your daily routine.
- Eliminate smoking to prevent circulation issues and further nerve damage.
- Reduce exposure to toxins that can worsen symptoms of neuropathy.
Conclusion
Some neuropathies that are caused by diabetes or alcohol can be stabilized with treatment, but the damage does not always heal. Focal neuropathy improves with treatment, often with complete resolution of symptoms. Over time, the severity of neuropathic pain can change, and a higher dosage of medication would continue to control the pain. Consider homeopathy, as it has no side effects and treats all symptoms naturally.
References
- Peripheral neuropathy [Internet]. National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. [cited 2024 Mar 1]. Available from: https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/disorders/peripheral-neuropathy
- Peripheral neuropathy [Internet]. nhs.uk. [cited 2024 Mar 1]. Available from: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/peripheral-neuropathy/
- Pomposelli, Raffaella & Piasere, Valeria & Andreoni, Cristina & Costini, Gavina & Tonini, Elena & Spalluzzi, Antonietta & Rossi, Daniela & Quarenghi, Chiara & Zanolin, Maria & Bellavite, Paolo. (2009). Observational study of homeopathic and conventional therapies in patients with diabetic polyneuropathy. Homeopathy : the journal of the Faculty of Homeopathy. 98. 17-25. 10.1016/j.homp.2008.11.006. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/23770235_Observational_study_of_homeopathic_and_conventional_therapies_in_patients_with_diabetic_polyneuropathy
- Mehra P, Sharma B, Baig H, Raveendar C, Prasad RVR, Rao MP, et al. Efficacy of homoeopathic treatment for diabetic distal symmetric polyneuropathy: A multicentric randomised double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. Explore (NY) [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2024 Feb 29];17(5):417–23. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32532601/
- Razzaq A, Hussain G, Rasul A, Xu J, Zhang Q, Malik SA, et al. Strychnos nux-vomica L. seed preparation promotes functional recovery and attenuates oxidative stress in a mouse model of sciatic nerve crush injury. BMC Complement Med Ther [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2024 Feb 29];20(1). Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12906-020-02950-3
- J. Goldstein, H.C. Winter, 3.27 – Mushroom Lectins, Elsevier, [cited 2024 Mar 1]. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-044451967-2/00153-7
- Ponnam, Hima Bindu. (2012). A Prospective Observational Study to ascertain the role of Homoeopathic therapy in the management of Diabetic Foot Ulcer. Indian Journal of Research in Homoeopathy. 6. 22-31.[cited 2024 Mar 1]. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/327916152_A_Prospective_Observational_Study_to_ascertain_the_role_of_Homoeopathic_therapy_in_the_management_of_Diabetic_Foot_Ulcer
- Raval, Heena & Bhatt, Gaurav. (2017). A Study to Ascertain the Utility of Kali phosphoricum in Diabetic Polyneuropathy. Homœopathic Links. 30. 059-061. 10.1055/s-0037-1599277. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/315510016_A_Study_to_Ascertain_the_Utility_of_Kali_phosphoricum_in_Diabetic_Polyneuropathy/citation/download
- Mehra P, Sharma B, Baig H, Raveendar C, Prasad RVR, Rao MP, et al. Efficacy of homeopathic treatment for diabetic distal symmetric polyneuropathy: A multicentric randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. Explore (NY) [Internet]. 2021;17(5):417–23. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.explore.2020.05.007