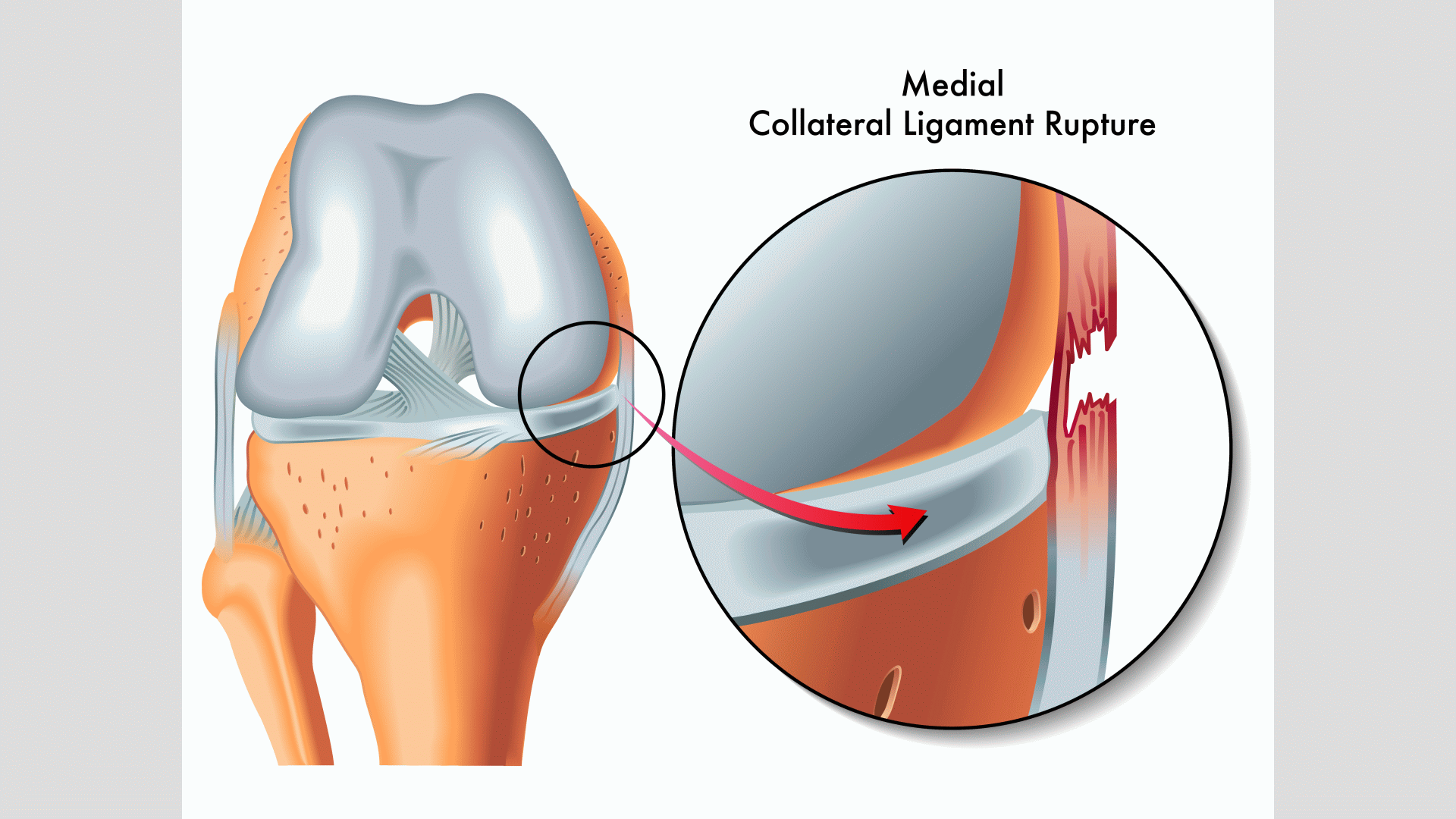
A ligament injury is the injury to tissue that binds the bones and the joints. These injuries happen mainly in the ankle, knee, elbow, or wrist. Ligament injuries are usually minor injuries that occur during sports, exercise, or other physical activity. They are associated with muscle tears. This injury occurs mainly in the muscles that support the calf, thigh, groin, and shoulder joints and there are many causative factors for ligament injury, acute injuries, chronic strain, and chronic conditions. Sometimes, ligament injuries and strains can be severe and require weeks of rehabilitation and physiotherapy.
Role of homeopathy ligament injury
Homeopathic medicine has proven effective in the prognosis and treatment of ligament injury. The homeopathic remedies for ligament injury treatment focus on stimulating the body’s natural healing mechanisms. They promote joint flexibility, reduce inflammation, and relieve stiffness. Improving blood supply around the tissues and ligaments further helps in healing at the earliest, and homeopathic medicine augments such a situation. Healing ligament injury improves the mobility of the joint.
Six effective homeopathic medicines for ligament injury
Symphytum officinale (Symph.)
Common name: Knitbone
Symphytum is an effective homeopathic medicine for treating sports injuries in athletes. It can be used routinely to promote the healing of fractures with ligament injuries, especially in cases where there is difficulty healing or torn muscles, tendons, or ligaments. Prolonged periosteal pain, even after wounds have healed, is the characteristic symptom of this remedy.
Hypericum perforatum (Hyper. Per.)
Common name: St John’s wort
Hypericum perforatum is indicated for wound healing. This remedy has action over nerve pain and knee contraction. This homeopathic medicine eases the pain after ligament injuries or trauma. Hypericum is indicated where ligament injury increases on climbing stairs up and down. The person feels relief from ligament injury by putting pressure on the knee joint. Pain increases in cold, dampness, foggy weather, and by touch.
Arnica montana (Arn. mont.)
Common name: Wolf’s bane
Arnica montana is indicated for every acute injury. It is used for its anti-inflammatory action in injuries when applied externally. This medicine is used in ligament injury with swelling, bruising, and inflammation in the ligament. There is soreness and pain in the knee joint and feet. Pain with bruise-like sensation in the joints. Pain is of throbbing, stinging type that worsens with the slightest touch.
Ruta graveolens (Ruta g.)
Common name: Rue-bitterwort
Ruta is indicated in tendinitis and ligament injuries. This remedy shows promising results in injuries that are hot when touched. This is indicated in injuries to the tendons, ligaments, cartilage, and connective tissues, and it may be used in injuries caused by excessively strenuous activity, where there may be lameness or weakness. Ruta is also helpful in injuries to the periosteum (covering of bones). It is used for curing puncture wounds and insect bites and removes pain in ligament Injuries. Injury pain is aggravated by damp, cold weather, by taking rest, and touching the impacted part. Initial movement is difficult while starting to walk, and symptoms are improved by movement and changing position, but continued motion does not bring relief.
Bellis perennis (Bellis per.)
Common name: Daisy
Bellis perennis is helpful for injuries of deeper tissues. Ligament injuries are caused by falling from a height, vehicle accidents, or surgery. Due to mechanical trauma, this medicine is helpful in venous congestion after ligament injury. The injured area feels stiff or cold. In a ligament injury near the thigh, the pain goes down the anterior of the thighs. The wrist feels contracted from an elastic band around the joint.
Colchicum autumnale (colch.)
Common name: meadow saffron
Colchicum autumnale is an effective remedy for ligament tear, where pain worsens in the evening. It naturally lowers pain after ligament injury and reduces the swelling and soreness in the joints. This medicine is indicated in cases of stiffness and swelling in multiple joints. Colchicum is well indicated when acute ligament injury appears with marked swelling and heat.
Causative factors of ligament injury
-
Acute traumatic ligament injuries
These injuries occur due to sudden impact or twisting of the leg usually seen in sports. There is direct trauma to the joints with wear and tear that causes ligament injury. Walking and playing after injury may cause swelling, ligament injury, and unstable gait.
-
Strain-induced injuries
Repetitive strain injuries and overuse of ligaments and joints can cause ligament injuries. Improper exercise, inadequate warm-ups, or excessive training without proper rest cause tissue damage and inflammation of the ligaments, resulting in ligament injury.
-
Obesity
Being overweight or obese is a common cause of ligament injury. During the twisting of the legs and wrist, obese people put excess weight on their ligaments, which causes damage to the tissue, ligaments, and cartilage.
Symptoms of ligament injury
Pain is the chief symptom. Other symptoms include knee swelling, hotness, hardness, and stiffness in the knee joint.
There may be swelling within the first few hours of the injury, body movement is restricted due to swelling and pain, loss of full range of motion, and discomfort while moving.
Diet and lifestyle modification for ligament injury
-
Vitamins and minerals
Vitamin C has excellent anti-inflammatory properties. Combining vitamin C with proteolytic enzymes provides better results in the healing of ligament injury. Collagen has ligament-healing properties. Vitamin C produces collagen. Vitamins B6 and B12 support nerve function and aid in forming amino acids.
Salmon, chicken, potatoes, sunflower seeds, spinach, bananas, beef, eggs, fortified cereals, and fortified soymilk are rich sources of Vitamin B, manganese, and protein. Zinc is excellent in combating inflammation. To prevent zinc deficiency, consume foods such as oysters and seafood. The body requires protein for the healing and reconstruction of tissues and ligaments. Protein is found in tofu, meat, eggs, and soy products.
-
Exercise
Exercise and yoga improve the strength of muscles and ligaments. Daily physical workouts make the body flexible and improve movements. Running, swimming, cycling, tracking, and outdoor sports are highly recommended to prevent ligament injury. Low-impact exercises are always beneficial. Losing weight can help you lower the chances of ligament injury.
Conclusion
Accurate diagnosis and effective treatment plans can contribute to reducing ligament injury and disability caused by it. Homeopathic medicines reduce pain and swelling from injured parts. However, discussing with a qualified homeopathic doctor before taking any medicine for safe and effective treatment is always advised. Rehabilitation with physiotherapy is essential to regain motion and strength.
References
- Motta MA. Scope and limitations of a ligament tear in homeopathy [Internet]. Ijrpr.com. [cited 2024 Feb 19]. Available from: https://ijrpr.com/uploads/V3ISSUE10/IJRPR7441.pdf
- Paris A, Gonnet N, Chaussard C, Belon P, Rocourt F, Saragaglia D, et al. Effect of homeopathy on analgesic intake following knee ligament reconstruction: a phase III monocentre randomized placebo controlled study. Br J Clin Pharmacol [Internet]. 2008 [cited 2024 Feb 19];65(2):180–7. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18251757/
- Sarembaud A. Ruta graveolens, a useful homeopathic medicine for musculoskeletal disorders. Rev d Homéopath [Internet]. 2017;8(2):e23–6. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.revhom.2017.03.008
- Staiger C. Beinwellwurzel: Von der Tradition zu modernen klinischen Studien. Wien Med Wochenschr [Internet]. 2013 [cited 2024 Feb 20];163(3–4):58–64. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10354-012-0162-4
- Sciencedirect.com. [cited 2024 Feb 20]. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/symphytum-officinale
- Aphale, Parth & Sharma, Dharmendra. (2022). Conventional Homeopathic Medicine and Its Relevance to Modern Medicine. Alternative therapies in health and medicine. 28.Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/361038475_Conventional_Homeopathic_Medicine_and_Its_Relevance_to_Modern_Medicine
- Schneider C, Schneider B, Hanisch J, van Haselen R. The role of a homoeopathic preparation compared with conventional therapy in the treatment of injuries: An observational cohort study. Complement Ther Med [Internet]. 2008;16(1):22–7. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ctim.2007.04.004
- Hacke D, Clausen J, Nicolai T, Riley DS, Fisher P, Mathie RT. Randomised controlled trials of homeopathy in humans: characterising the research journal literature for systematic review. Homeopathy [Internet]. 2013;102(01):3–24. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.homp.2012.10.002
- Galeotti N. Hypericum perforatum (St John’s wort) beyond depression: A therapeutic perspective for pain conditions. J Ethnopharmacol [Internet]. 2017;200:136–46. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2017.02.016
- Knuesel O, Weber M, Suter A. Arnica montana gel in osteoarthritis of the knee: An open, multicenter clinical trial. Adv Ther [Internet]. 2002 [cited 2024 Feb 20];19(5):209–18. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12539881/
- Karakas FP, Karakas A, Boran C, Turker AU, Yalcin FN, Bilensoy E. Wound healing activity of the Bellis perennis L. (common daisy). N Biotechnol [Internet]. 2012;29:S142. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2012.08.395