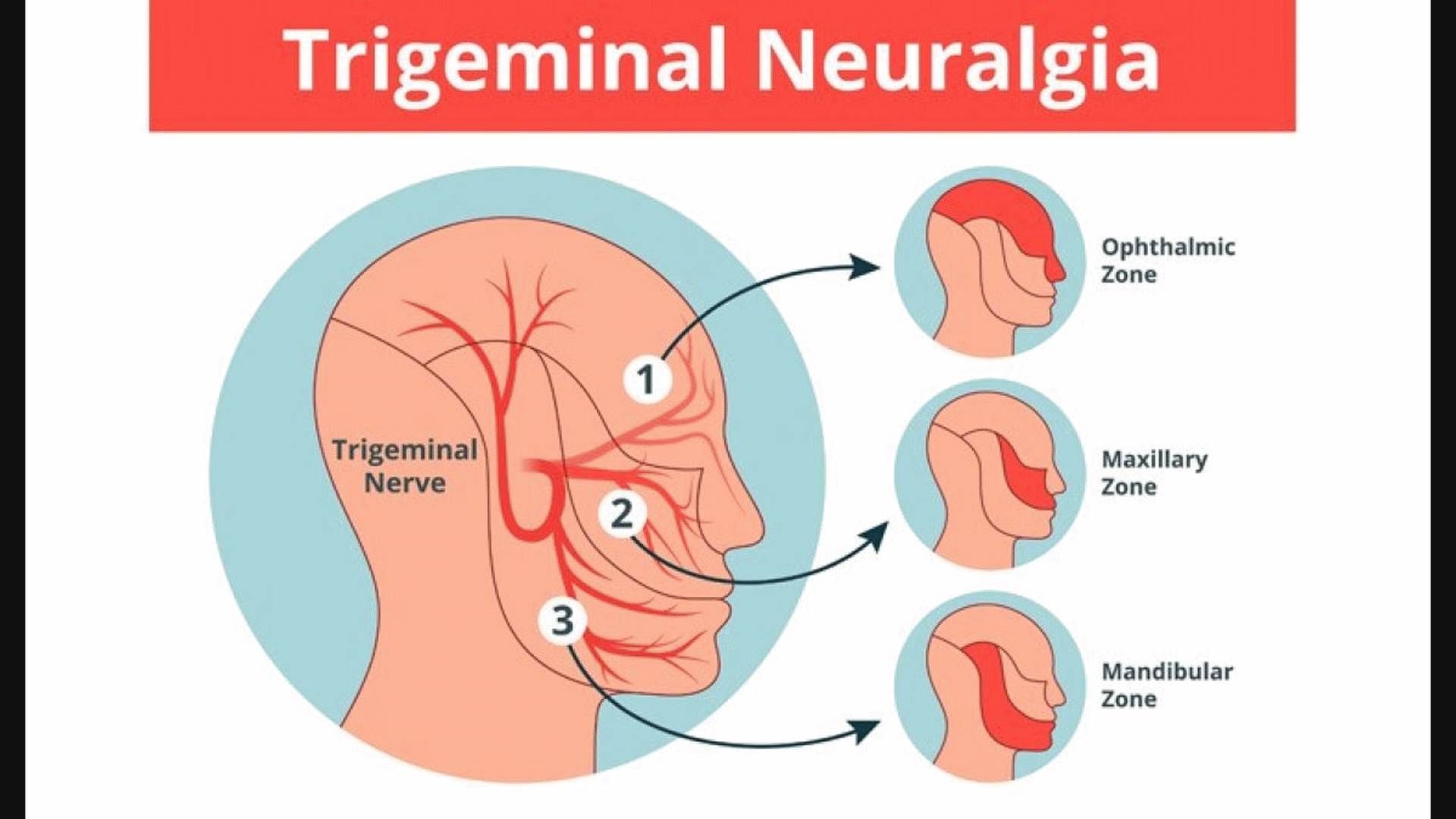
Trigeminal neuralgia is a condition causing intense facial pain same as an electric shock on one side of the face. The trigeminal nerve is one of the twelve pairs of nerves attached to the brain. It transmits touch and pain sensations from your face and head to the brain. Trigeminal neuralgia episodes are short-lived, but the pain can return sporadically. The condition can be long-lasting and is known as a chronic pain condition.
Typically, trigeminal neuralgia is unilateral, which only affects one side of your face. Bilateral trigeminal neuralgia is very rarely found, although it can affect both sides but not at the same time. There are two main types of trigeminal neuralgia – typical (type 1) trigeminal neuralgia, in which the episodes are very painful, sharp, intense, and sporadic. You may feel burning and pain all over your face, which lasts up to a few seconds to two minutes.
The other is atypical (type 2) trigeminal neuralgia, which is less painful but more widespread. You’ll feel constant pain, like stabbing or burning sensations, with persistent aches and pains. The symptoms of atypical trigeminal neuralgia are more difficult to control. Trigeminal neuralgia is also known as tic douloureux. It usually affects people over the age of 50. The condition also affects women more than men and is considered a rare disorder.
Role of homeopathy in trigeminal neuralgia
Homeopathic medications help to reduce the recurrence, intensity, and frequency of the attacks of trigeminal neuralgia, which also fades away with time. The trigeminal nerve is the 5th head nerve of the face and has three divisions: the ophthalmic branch, the maxillary branch, and the mandibular branch. One or more of the three branches of the nerve may be affected. Homeopathic medicines help provide relief from the symptoms like pain and numbness.
Five effective homeopathic medicines for trigeminal neuralgia
Belladonna
Common name: Deadly nightshade
Belladonna helps in managing right-sided facial pain of trigeminal neuralgia. It can be used both in acute and chronic conditions. The pain is marked on the right temple, going to the eye and cheek on the right side. The acute episodes are very sudden and violent in nature. The trigeminal neuralgia pain is triggered by touch and face movement and is relieved from hard pressure over the affected area. It is helpful when pain occurs in the jaw, teeth, and ears. A marked burning sensation with redness may accompany the above symptoms.
Colocynthis
Common name: Bitter or squirting cucumber
Colocynthis works effectively in cases of trigeminal neuralgia where the pains are violent, shooting, and stitching in character. Numbness may follow neuralgic pain, which gets better by pressure. There are tearing pains in the cheeks and stitches in the upper jaw that recur frequently. The left side of the cheek, temple, ear, and the side of the neck may get affected. Facial neuralgia and toothache remain restricted to one side.
Magnesia phosphorica
Common name: Magnesium phosphate
Mag. phos. is indicated for cases of right-sided trigeminal neuralgia. Pain typically starts near the right eye and extends to the entire right side of the face. The pain is sharp, shooting, cutting, and is almost unendurable. The pain darts along the course of the nerve like a lightning flash and rapidly changes place. Pain may return every two to three hours. Right-sided pain of the face may alternate with a toothache. It may get worse by a draft of cold air, motion, slightest touch, or cold application. The patient may get relief from the heat and warm application.
Spigelia
Common name: Pink root
Spigelia is indicated for left-sided trigeminal neuralgia. Facial pain on the left side of the face that comes and goes suddenly is commonly seen. The area around the left eye, forehead, cheek, teeth, and temple are particularly painful. The pain is shooting, burning, and tearing in nature. The trigeminal neuralgia attack arises from cold air, water, and rainy weather and is relieved by pressure. Spigelia can be used when ophthalmic and maxillary branches of the trigeminal nerve are affected.
Verbascum thapsus
Common name: Mullein
Verbascum is a medicine for trigeminal neuralgia that has an action on the maxillary branch of the trigeminal nerve. The periodic facial pain is tearing, stitching, cramping, and crushing. The neuralgia is on the left side of the face, temporomandibular (jaw) joint, and ear. Pain occurs in flashes, and pressure in the entire left side of the head and face may be present. Pain gets triggered by sneezing, talking, and change of weather. There is a severe pressing and pinching pain on the side of the lower jaw.
Causative factors for trigeminal neuralgia
Trigeminal neuralgia is typically caused by blood vessels exerting pressure on the nerve near the brainstem. A tumor pressing against the trigeminal nerve might also cause trigeminal neuralgia. If your trigeminal nerve is damaged due to oral sinus surgery, stroke, facial trauma, or injury due to surgery, it can also cause trigeminal neuralgia.
Triggers for trigeminal neuralgia:
- Touching your face while shaving, washing your face, or putting on makeup
- Eating and drinking
- Brushing, flossing, or using mouthwash
- Talking or smiling
- Applying pressure to your face, especially your cheeks or jawline
- A strong wind or breeze blowing on your face
Symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia
- Intense shooting or electric-type pain
- Sudden episodes of pain are triggered by touching the face, speaking, chewing, or brushing your teeth.
- Pain episodes persisting from a few seconds to several minutes.
- Pain occurs with facial spasms.
- Numbness or tingling sensation.
- A burning sensation all over one side of the face.
- Pain episodes that become more frequent and intense over time.
Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia
Treatment for trigeminal neuralgia includes medications like muscle relaxants, anti-seizure medicines, and botox injections to relieve the pain. Surgical treatment is indicated when the condition does not respond to medical management. It includes surgical techniques such as balloon compression, glycerol injection, microvascular decompression, and stereotactic radiosurgery based on the severity of your pain, physical health, preference, or previous surgeries.
Diet and lifestyle modifications for trigeminal neuralgia
- Eat soft and easy to chew foods to avoid trigger attacks.
- Avoid stimulants like caffeine, citrus, cold foods, sweet, and spicy foods that may trigger an attack.
- Rinse the mouth with room temperature water.
- Use warm or cold compresses to relieve the pain.
Conclusion
Trigeminal neuralgia is a chronic condition where the prognosis varies from person to person. Some people may experience long periods of remission with little or no pain, while others may have persistent or recurrent pain. The severity and frequency of pain episodes can also fluctuate with time.
It is essential to follow up with your healthcare professional to develop a comprehensive treatment plan for trigeminal neuralgia and allow symptoms to be monitored. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and exploring various available treatments are crucial steps in managing trigeminal neuralgia. Homeopathic remedies help relieve the pain and numbness involved in trigeminal neuralgia.
References
- Mojaver YN, Mosavi F, Mazaherinezhad A, Shahrdar A, Manshaee K. Individualized homeopathic treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: an observational study. Homeopathy. 2007;96(2):82-86. doi:1016/j.homp.2007.02.006
- Verma, Narayan & Sherwood, Frank. (2013). Low saturated fat diet is effective in trigeminal neuralgia. Open Journal of Preventive Medicine. 03. 402-406. DOI: 4236/ojpm.2013.36054.
- Trigeminal neuralgia [Internet]. Hopkinsmedicine.org. 2023 [cited 2024 Mar 16]. Availablefrom:https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/trigeminal-neuralgia
- Trigeminal neuralgia [Internet]. nhs.uk. [cited 2024 Mar 16]. Available from: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/trigeminal-neuralgia/
- Shankar Kikkeri N, Nagalli S. Trigeminal Neuralgia. [Updated 2022 Jul 9]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554486/
- Sanadhya, Yatish & Sudhanshu, Sanadhya & Sharma, Nidhi & Jain, Sorabh & Aapaliya, Pankaj & Choudhary, Garima. (2013). HOMEOPATHY A COMPLIMENT TO DENTISTRY – A REVIEW. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/279765996_HOMEOPATHY_A_COMPLIMENT_TO_DENTISTRY_-_A_REVIEW
- Polan M. Pain Control: Trigeminal Neuralgia—A Review of Etiology and Treatment. Anesthesia Progress.1966Sep;13(7):229. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2235328/pdf/anesthprog00217-0027.pdf