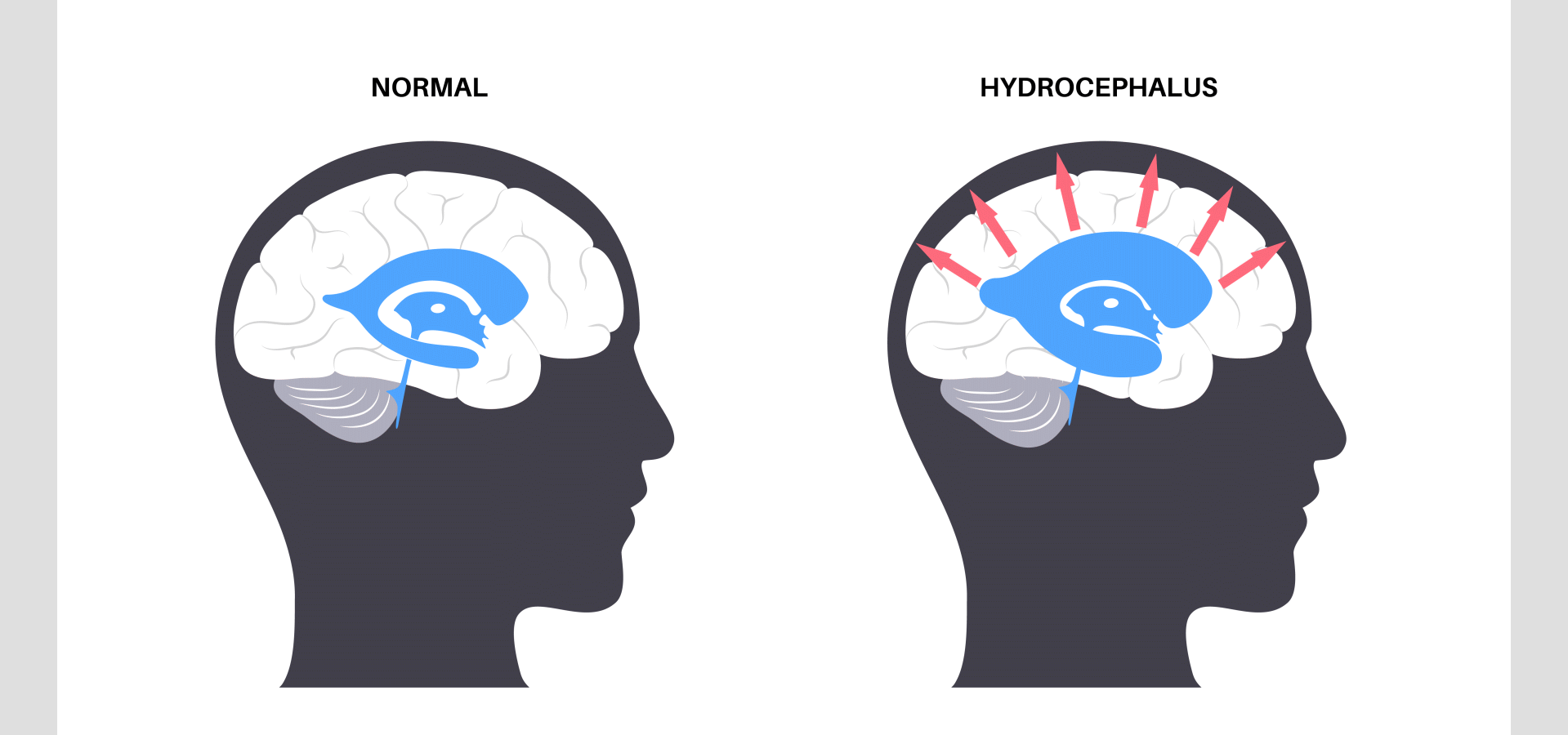
Hydrocephalus refers to a condition in which there is too much buildup of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the cavities called ventricles of the brain. CSF is a colorless fluid that helps cushion the brain. The tissues surrounding the ventricles produce CSF. Cerebrospinal fluid usually flows through the ventricles, brain, and spinal cord. It provides nutrients to the brain and acts as a shock absorber in cases of injury. It then gets absorbed in the blood.
Cerebrospinal fluid constantly goes through the cycle of production and reabsorption. When CSF production increases, the size of the ventricles increases and this exerts pressure on the brain, causing brain tissue damage. Hydrocephalus can cause symptoms related to brain dysfunction and developmental issues. The size of the head grows disproportionately and can visibly bulge out due to the accumulation of CSF.
Hydrocephalus can occur at any age but is common in infants and older adults above 60 years of age. This condition tends to affect approximately one to two in every 1000 babies. The majority of cases of hydrocephalus are often diagnosed at the time of delivery or in early childhood.
Role of homeopathy in hydrocephalus
Homeopathic treatment can help improve the normal functioning of CSF production and absorption in the brain and prevent hydrocephalus. In cases of excess hydrocephalus, homeopathic medicines are able to reduce the excess production of CSF. In cases of poor absorption, homeopathic medicines are able to improve the absorption of CSF in the blood and can help reduce the accumulation of CSF. This helps to maintain the balance and the brain to develop in a normal and healthy way.
Homeopathy provides symptomatic treatment in cases of hydrocephalus. There are numerous natural homeopathic medicines to manage hydrocephalus, and the medicines are selected based on an individual’s symptoms. Try consulting a homeopathic specialist who can prescribe the medications for hydrocephalus after taking the detailed case and analyzing each individual case.
Five effective homeopathic medicines for hydrocephalus
Apis mellifica (Apis.)
Common name: Honey bee
Apis. helps manage acute cases of hydrocephalus in children. The child’s head appears large with prominent eyes. They may have a squint in one or both eyes. The child is very irritable, nervous, and fidgety. Difficulty in concentrating while attempting to study. There may be sudden screams of cry while waking or sleeping. The child is very lethargic and weak, with low energy levels. There is excessive sleep and the child is always in a semiconscious state with eyes partly closed. There is bag-like swelling under the lower eyelids with burning and stinging pain. The child rolls their head from side to side with one side of the body twitching and jerking of limbs. There is frequent urination, which is painful, and while urinating, the last drop burns. Apis is also indicated for seizures in hydrocephalus. The complaints are worse in warm and heated rooms and better in the open.
Calcarea carbonica (Calc. carb.)
Common name: Calcium carbonate
Calc. carb. helps in managing hydrocephalus when the head is too large. The children needing this medicine have delayed closing of fontanelles and sutures. They usually have a tendency for the head and neck to sweat profusely. There is a cold feeling all over with sensitivity to cold. The head is large and the abdomen is swollen. The baby has delayed milestones.
Helleborus niger (Helleborus)
Common name: Christmas rose
Helleborus is used in cases of meningitis, encephalitis, and hydrocephalus. The look of the child is thoughtless and staring with wide eyes open. He has a deep sleep with occasional screams. He may have trembling hands. There may be impaired vision and speech difficulty. The child is very much irritable and easily angered. During these troubles, there is convulsion with the extreme coldness of the body. The child rolls their head from side to side frequently.
Artemisia vulgaris (Artemisia vulg.)
Common name: Mugwort
Artemisia helps in managing convulsions in hydrocephalus. It is used when seizures occur with hydrocephalus. The seizures frequently occur by bending the head backward or sideways. Seizures can occur from a fall or blow on the head, and the attacks are frequently repeated with long intervals of rest.
Kalium iodatum (Kali. hydriodicum)
Common name: Potassium iodide
Kali. iod. is used when there is squinting of eyes present with other symptoms of hydrocephalus. The symptoms include crying, vomiting, and pain in the forehead with trembling of limbs. Occasional seizures are present.
Causative factors for hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus can occur when there is an imbalance between the amount of CSF produced and the amount of CSF absorbed in the bloodstream. The causes are as follows:
- When there is an obstruction in the normal flow of the CSF within the ventricles or from the ventricles to the brain, there is an excess in the amount of CSF produced. This is known as non-communicating or obstructive hydrocephalus.
- When there is an improper absorption of CSF, it is known as communicating or non-obstructive hydrocephalus.
- When the CSF is produced at a higher rate than it is being absorbed, there is excess accumulation of CSF.
Most of the cases, the exact cause of hydrocephalus is unknown. However, developmental or medical conditions can contribute to triggering hydrocephalus.
In newborns, hydrocephalus can develop shortly after birth or even before the baby is born. Associated reasons include a congenital disability such as blockage that may happen in the passage between ventricles, leading to accumulation of the fluid. Certain infections like rubella and syphilis in the uterus during pregnancy and bleeding in the brain during delivery may result in hydrocephalus.
Hydrocephalus can develop due to infections like meningitis, trauma or injury to the brain, or tumors of the brain or spinal cord.
Signs and symptoms of hydrocephalus
-
Infants
In infants, hydrocephalus may cause an increase in the size of the head or bulging of fontanelles on the head. The head appears larger than usual, and the eyes are fixed downwards, known as the sunsetting of the eyes. The babies are very irritable and cranky, with poor appetite. Other symptoms of hydrocephalus include seizures, vomiting, weakness, or decreased muscle strength. There may be excessive sleepiness involved. Babies born with hydrocephalus may have delayed milestones and memory problems. There may be epilepsy and issues related to physical coordination.
-
Toddlers and older children
Hydrocephalus in older children can cause chronic headaches, tiredness, and loss of coordination. The symptoms of hydrocephalus also include a drop in memory and difficulty in concentration, which can affect future performance. There may also be vision changes or loss of bladder control, irritability and personality changes.
-
Young and middle-aged adults
The symptoms include chronic headaches, tiredness, and problems walking. There is difficulty concentrating with weak memory and symptoms such as loss of bladder control and vision disturbance.
-
Older adults (aged above 60 years)
Hydrocephalus can cause symptoms such as frequent urination or loss of bladder control. Memory loss, problems with balance and coordination while walking.
Treatment and management of hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus may be treated directly by removing the cause of the CSF obstruction or indirectly diverting the excess fluid to other areas of the body. The standard treatment for hydrocephalus includes implanting a device known as a “shunt.” It is used to divert the excess CSF away from the brain to the body cavity such as abdominal organs or peritoneal cavity. The shunt consists of a small flexible tube with a catheter and a valve, which is placed to drain excess fluid. Once the shunt is inserted, it remains in the body for the rest of the duration of life.
The shunt performs continuously, thereby keeping the CSF within normal limits. In cases of brain tumors, two procedures are performed –first to divert the CSF and second to remove the tumor. There are a few cases of hydrocephalus where the patients can be treated with a procedure called endoscopic third ventriculostomy. While performing the procedure, the surgeon utilizes a tiny camera (endoscope) with fiber optics to visualize the ventricles and create a new pathway for the CSF to flow.
The treatment of hydrocephalus requires long-term care and follow-up. Even after the appropriate placement of a shunt, annual visits are mandatory.
Diet and lifestyle modifications for hydrocephalus
A healthy lifestyle, including a healthy weight, regular exercise, and cognitive therapies, may help in hydrocephalus. Foods like green leafy vegetables, nuts, whole, beans, grains, fish, olive oil, and poultry may have nutritional benefits. Avoid eating red meats, sugary foods, fried and processed foods.
Coping with the symptoms of hydrocephalus can be difficult. The condition affects every aspect of your life, including family, work, social life, and financial status. You may sometimes feel overwhelmed, depressed, angry, or resentful. Join support groups to help you deal with these emotions. These groups of people share things and want to help themselves by sharing coping strategies to deal with hydrocephalus. You can ask your healthcare provider to find a group that works for you.
Conclusion
People with hydrocephalus can lead a normal and healthy life with surgery, monitoring, and few conventional treatments. The condition and complications from surgery vary from person to person. It is important to work with your healthcare provider to get the care you need. Homeopathic medicines provide symptomatic relief. While using a homeopathic approach, each individual case is different from that of others. It is important to consult a homeopathic physician before self-medicating. The medicines for hydrocephalus are from safe and natural sources and have a positive effect on cases of hydrocephalus.
References
- Hydrocephalus [Internet]. National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. [cited 2024 Feb 19]. Available from: https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/disorders/hydrocephalus
- Hydrocephalus [Internet]. Aans.org. [cited 2024 Feb 19]. Available from: https://www.aans.org/en/Patients/Neurosurgical-Conditions-and-Treatments/Hydrocephalus
- Hydrocephalus [Internet]. Hopkinsmedicine.org. [cited 2024 Feb 19]. Available from: https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/hydrocephalus
- Koleva M, De Jesus O. Hydrocephalus. StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Available from:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560875/
- Hydrocephalus [Internet]. nhs.uk. [cited 2024 Feb 19]. Available from: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/hydrocephalus/
- HA Stories from Parents, Hydrocephalus Stories, Stories NPH. What is hydrocephalus? [Internet]. Hydrocephalus Association. 2023 [cited 2024 Feb 19]. Available from: https://www.hydroassoc.org/about-hydrocephalus/
- Ekiert H, Pajor J, Klin P, Rzepiela A, ?lesak H, Szopa A. Significance of Artemisia vulgaris L. (common mugwort) in the history of medicine and its possible contemporary applications substantiated by phytochemical and pharmacological studies. Molecules [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2024 Mar 3];25(19):4415. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194415
- Wessell, Aaron & Kole, Matthew & Cannarsa, Gregory & Oliver, Jeffrey & Jindal, Gaurav & Miller, Timothy & Gandhi, Dheeraj & Parikh, Gunjan & Badjatia, Neeraj & Aldrich, E. & Simard, J Marc. (2018). A sustained systemic inflammatory response syndrome is associated with shunt-dependent hydrocephalus after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Journal of Neurosurgery. 130. 1-8. 10.3171/2018.1.JNS172925. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/326074285_A_sustained_systemic_inflammatory_response_syndrome_is_associated_with_shunt-dependent_hydrocephalus_after_aneurysmal_subarachnoid_hemorrhage/citation/download