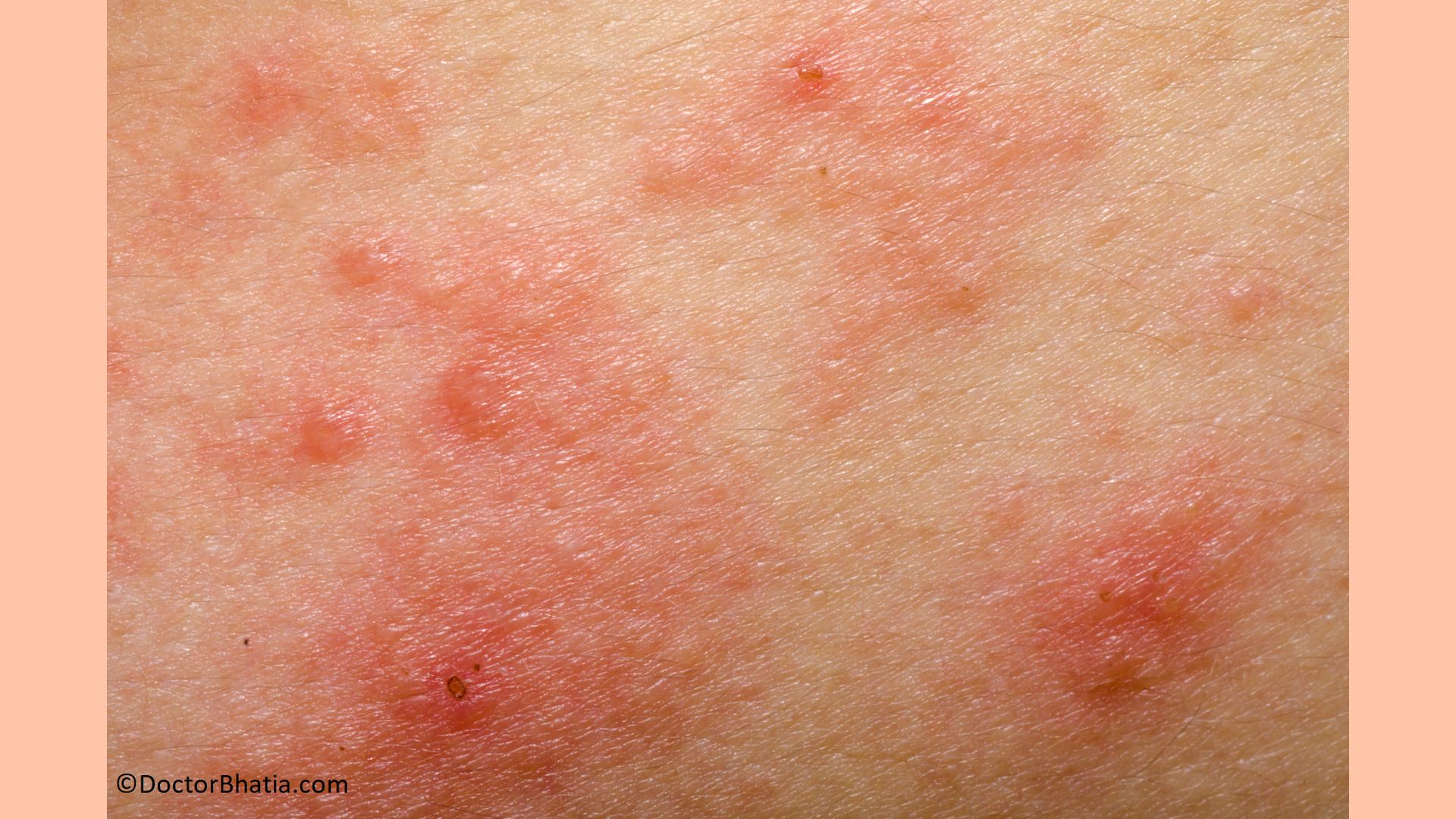
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by dry, red, scaly, and itchy skin. It is a non-contagious disease that does not spread from one person to another. This condition mostly begins in childhood before the age of five years and may only continue till adulthood in a few cases. When this eczema affects infants, it is called infantile eczema.
There are two phases of atopic dermatitis.
- Remitting phase during which skin inflammation clears off
- Relapsing phase during which the skin condition flare-ups
Mostly, these are treated with local or oral steroids, which give temporary relief. However, atopic dermatitis can be effectively treated with homeopathy. Made from natural substances, homeopathic remedies aid in healing eczema eruptions, lessen the severity, and reduce flare-ups.
Role of homeopathy in atopic dermatitis
Homeopathic medicine for atopic dermatitis includes knowing the site of eruption, the type of atopic dermatitis, the factors that aggravate and ameliorate, time of itching, and severity of itching. It also considers your food desires and aversions, sensitivity to heat and cold, mental disposition, and other physical symptoms.
Homeopathic medicines help reduce the severity of atopic dermatitis, itching, and its frequent relapses.
Top five homeopathic medicines for atopic dermatitis
Homeopathy is an individualistic solution. Thus, one medication will not cure all atopic dermatitis cases. Also, you may not get instant relief and may take some time. This time depends upon the severity, duration of atopic dermatitis, and the person’s individual response. But in the end, it gives worthy results. Here are the top five homeopathic remedies for atopic dermatitis.
Graphites naturalis (Graph.)
Common name: Black lead
A good homeopathic medicine for managing atopic dermatitis is Graphites. This remedy helps in eczema with dry, rough skin that often cracks.
Graphites is indicated for atopic dermatitis over the bends of elbows or bend of knees, neck, and behind the ears. This medicine is effective in facial, nose, and chin eczema. This remedy works well on atopic dermatitis with skin vesicles filled with fluid that ooze sticky, gluey discharge.
Sulphur (Sulph.)
Common name: Sublimated Sulphur
Atopic dermatitis with intense itching can be treated with the homeopathic medicine Sulphur. This remedy treats atopic dermatitis that have itching and burning sensation that worsens by scratching, washing, and in the heat.
Sulphur is suited for atopic dermatitis with excessively dry scales that itch at night when the person’s body gets warm in bed. Relapsing eczema in the spring season or damp weather calls for this remedy. Experts prescribe this remedy for atopic dermatitis suppressed by local ointments or external applications.
Hepar sulphuris calcareum (Hep.)
Common name: Hahnemann’s calcium sulfide
Hepar sulph. is a very good homeopathic medicine for eczema with suppuration or pus formation. It is indicated in atopic dermatitis with intense itching in the area affected. Hepar sulph. skin is often deep cracked. This remedy cures atopic dermatitis lesions that are sensitive to touch.
These people are sensitive to cold air to the extent that the person cannot uncover himself even for a moment. Sensitivity to temperature changes is so high in them, that an open door in the other room will make them feel cold, and they often start reacting or sneezing.
Petroleum (Petr.)
Common name: Crude rock oil
Petroleum is a very good homeopathic medicine for eczema with extremely dry skin that tends to crack. This remedy is indicated for atopic dermatitis on fingertips and palms.
This medicine is prescribed for atopic dermatitis that worsens in winter, with deep, sore bleeding cracks.
Petroleum treats itching skin lesions that worsen at night due to the warmth of the bed. These rashes turn reddish and ooze fluid or remain dry. This remedy treats genital eczema in males and genital eczema in females that breaks out during menses. The petroleum skin gets easily infected and forms tough, leathery scabs due to chronic irritation.
Mezereum (Mez.)
Common name: Spurge olive
Mezereum is a very good homeopathic remedy for atopic dermatitis eruptions with sticky fluid discharge. It is indicated in atopic dermatitis with a thick scab on the skin with pus under it, indicating infection.
This remedy is suited for eczema in the scalp with a thick leather-like crust. There is intense itching, and when the person scratches, blood oozes out of it. Other indications of this remedy include atopic dermatitis worse from bathing with warm water, itching worsening in the bed, and eczema better in the open air.
Causes of atopic dermatitis
The exact cause of atopic dermatitis is not known. However, a combination of genetic and environmental factors are thought to cause eczema. Some common causative factors causing atopic dermatitis are mentioned below:
Genetics
Atopic dermatitis runs in families. Suppose either parent has eczema or any other allergic condition, such as asthma, urticaria, a food allergy, a pollen allergy, etc. The child may be more prone to get atopic dermatitis in that case.
Environmental factors
People residing in colder climates and urban regions with high pollution levels are more prone to get atopic dermatitis.
Physical factors
Some external factors that may cause atopic dermatitis include frequent use of synthetic garments, exposure to harsh soaps and detergents, dyes, chemicals, cosmetics like deodorants and bleach, and metals like nickel and copper.
Altered immunity
An aberrant immune system response to specific internal or environmental factors can cause atopic dermatitis. When you come into contact with a trigger, your immune system interprets minor irritants as dangerous foreign invaders like bacteria or viruses.
Drugs
Some conventional medications, when used over a prolonged period, can potentially cause atopic dermatitis.
Stress
Your emotional well-being could impact your skin health, leading to the escalation of atopic dermatitis. You may experience eczema flare-ups more frequently if you have high levels of stress, anxiety, or depression.
Symptoms of atopic dermatitis
Symptoms of this type of atopic dermatitis differ substantially from person to person. Also, symptoms vary in their intensity from mild to severe. The common symptoms of atopic dermatitis are:
- Dryness of skin
- Intense and severe itching
- Inflammation and swelling
- Redness of the skin
- Red, brown, purple, or gray coloured rashes
- Small vesicles filled with fluid
- Oozing fluid that is sticky
- Blood oozing from bumps
Treatment for atopic dermatitis
Topical steroid creams
Corticosteroid creams and ointments can help heal your skin and decrease itching. They should be used exactly as instructed because wrong use might result in side effects, including thinning skin or pigment loss.
Oral steroids
If the inflammation is severe, Prednisone or other oral corticosteroids are prescribed. Due to possible adverse effects such as excessive blood sugar, glaucoma, decreased growth in children, and slower wound healing, these medications are only used temporarily.
Antibiotics, antivirals, or antifungals.
If atopic dermatitis infects, the doctor will prescribe these medications to treat the infection and relieve your symptoms.
Wet dressings
In this approach, steroid creams are applied, followed by wet bandages. This mode of treatment is given in case of atopic dermatitis flare-ups.
Light therapy
Those who experience severe flare-ups after receiving conventional therapies benefit from light therapy. During this treatment, a moderate amount of UV light is used. Long-term use of this medication may raise the risk of skin cancer and early aging.
Diet and lifestyle modifications for atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis can be distressing due to itching and flare-ups. Although over-the-counter (OTC) creams and medications can help you reduce symptoms, some dietary and lifestyle changes can prevent atopic dermatitis from worsening.
Fish
Omega-3 fatty acids, naturally found in fish, can help reduce inflammation in atopic dermatitis.
Probiotic food
Probiotics are naturally occurring bacteria that support your gut health. According to research, these foods decrease inflammation that can cause atopic dermatitis.
Foods high in flavonoids
Many foods include flavonoids, which are anti-inflammatory substances. They are commonly present in colorful fruits and vegetable skins, like tomatoes, bell peppers, citrus fruits, berries, and green tea.
Food rich in vitamin C
Include foods rich in diet Vitamin C, like bell peppers, strawberries, oranges, cauliflower, pineapple, and mangoes. Antioxidants in vitamin C help shield your body from allergic reactions.
Food rich in potassium
Bananas, avocados, squash, sweet potatoes, white beans, salmon, and sweet potatoes are high in potassium. This nutrient reduces inflammation and eases atopic dermatitis symptoms.
Conclusion
Identifying causative allergen for atopic dermatitis and removing it from your environment is not a practical solution. With homeopathy, you can increase your immunity to fight against the allergen. Thus, the results of homeopathic medicines for atopic dermatitis are safe, long-lasting, and effective.
References
- Brown S, Elias M, Bradley M. Genetics in atopic dermatitis: Historical perspective and future prospects. Acta Derm Venereol [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2023 Oct 8];100(12):adv00163. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.2340/00015555-3513
- Kantor R, Silverberg JI. Environmental risk factors and their role in the management of atopic dermatitis. Expert Rev Clin Immunol [Internet]. 2017 [cited 2023 Oct 8];13(1):15–26. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/1744666x.2016.1212660
- Kim K. Influences of environmental chemicals on atopic dermatitis. Toxicol Res [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2023 Oct 8];31(2):89–96. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.5487/tr.2015.31.2.089
- Boguniewicz M, Leung DYM. Atopic dermatitis: a disease of altered skin barrier and immune dysregulation. Immunol Rev [Internet]. 2011 [cited 2023 Oct 8];242(1):233–46. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-065x.2011.01027.x
- Arndt J, Smith N, Tausk F. Stress and atopic dermatitis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep [Internet]. 2008 [cited 2023 Oct 8];8(4):312–7. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18606083/
- Gabros S, Nessel TA, Zito PM. Topical Corticosteroids. StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532940/
- Drucker AM, Eyerich K, de Bruin-Weller MS, Thyssen JP, Spuls PI, Irvine AD, et al. Use of systemic corticosteroids for atopic dermatitis: International Eczema Council consensus statement. Br J Dermatol [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2023 Oct 8];178(3):768–75. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/bjd.15928
- Sawada Y, Saito-Sasaki N, Nakamura M. Omega 3 fatty acid and skin diseases. Front Immunol [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 Oct 8];11. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.623052
- Rusu E, Enache G, Cursaru R, Alexescu A, Radu R, Onila O, et al. Prebiotics and probiotics in atopic dermatitis (Review). Exp Ther Med [Internet]. 2019 [cited 2023 Oct 8];18(2):926. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.3892/etm.2019.7678
- Kawai M, Hirano T, Higa S, Arimitsu J, Maruta M, Kuwahara Y, et al. Flavonoids and related compounds as anti-allergic substances. Allergol Int [Internet]. 2007;56(2):113–23. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1323893015308558
- Chambial S, Dwivedi S, Shukla KK, John PJ, Sharma P. Vitamin C in disease prevention and cure: An overview. Indian J Clin Biochem [Internet]. 2013 [cited 2023 Oct 8];28(4):314–28. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12291-013-0375-3
- Costa RO, Macedo PM de, Carvalhal A, Bernardes-Engemann AR. Use of potassium iodide in Dermatology: updates on an old drug. An Bras Dermatol [Internet]. 2013 [cited 2023 Oct 8];88(3):396–402. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/abd1806-4841.20132377
- Researchgate.net. [cited 2023 Oct 8]. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/236272955_Atopic_Dermatitis_and_Homeopathy
- Researchgate.net. [cited 2023 Oct 8]. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/357564728_Efficacy_of_graphites_6c_in_treating_chronic_eczema_A_case_study
- Eizayaga JE, Eizayaga JI. Prospective observational study of 42 patients with atopic dermatitis treated with homeopathic medicines. Homeopathy [Internet]. 2012 [cited 2023 Oct 8];101(1):21–7. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22226311
- Van Wassenhoven M. Clinical verification in homeopathy and allergic conditions. Homeopathy [Internet]. 2013 [cited 2023 Oct 8];102(01):54–8. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23290880/