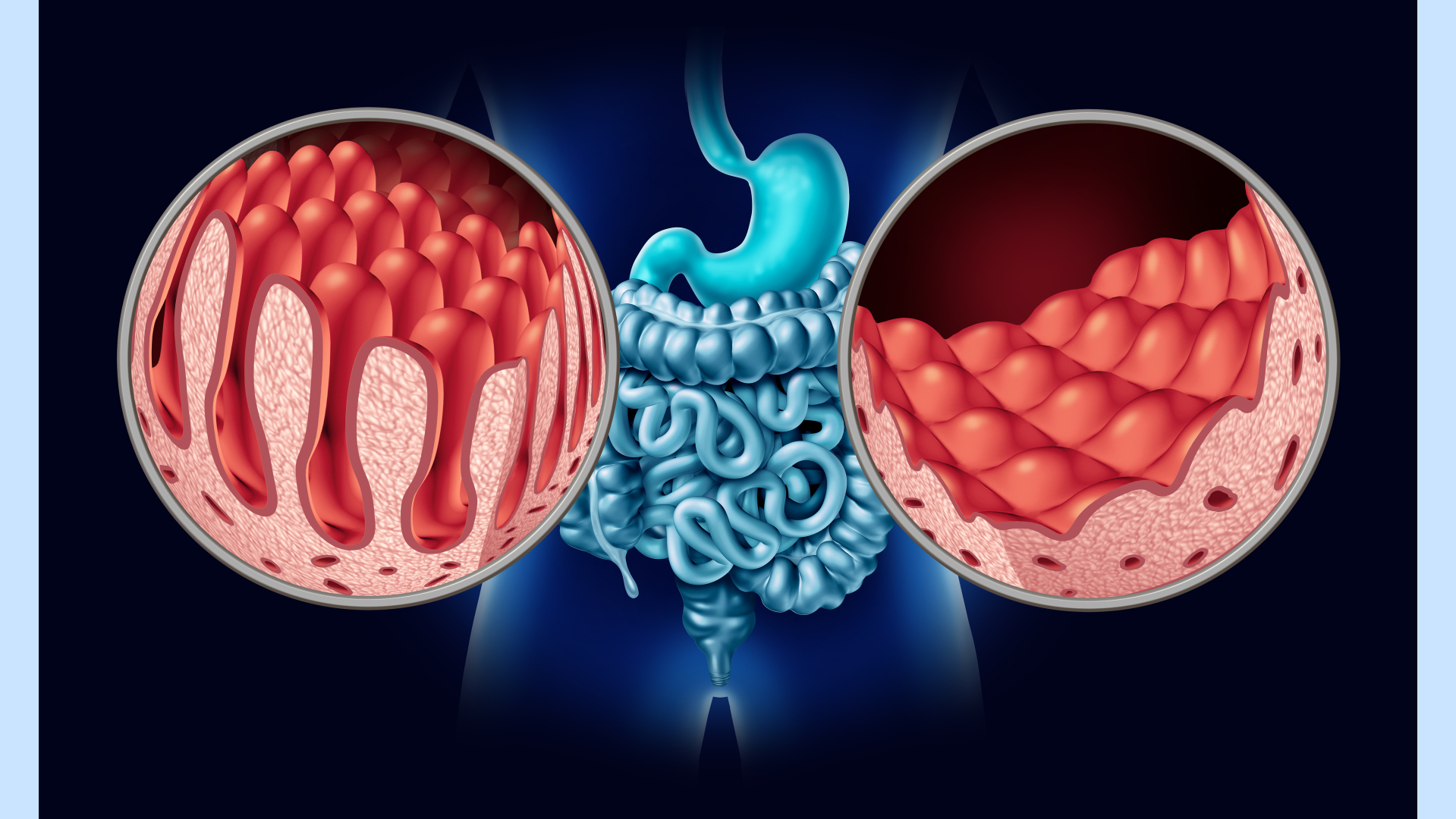
1% of the world’s population, which is approximately 70,000,000, is suffering from celiac disease. This is a gastric condition in which eating gluten triggers an immune response. Gluten is a protein present in grains like wheat, rye, and barley. Gradually, this immune response causes inflammation that damages the lining of your small intestine. The damaged small intestine prevents the absorption of some nutrients, causing nutritional deficiencies.
Your small intestine is lined with minute finger-like structures called villi. These villi absorb the nutrients present in the food you eat. Nutrient absorption is hindered when these villi get damaged by your immune response in celiac disease. This leads to minerals, vitamins, and other nutrient deficiencies.
You might experience symptoms like abdominal pain, diarrhea, bloated abdomen, weight loss, and cramps. Due to malabsorption, you might develop anemia, fatigue, and deficiency of iron, zinc, copper, and selenium. Celiac disease hinders growth and development in children.
The exact cause of celiac disease is not known. However, genetic predisposition is considered to be the causative factor. The only way to treat celiac disease is by eliminating gluten from your diet.
However, gluten sensitivity can be reduced with homeopathy. When prescribed on your individual symptoms, these medicines reduce the intensity, frequency, and severity of celiac disease symptoms. It provides natural, safe, and long-lasting relief from celiac disease.
Role of homeopathy in celiac disease
In celiac disease, the gluten-triggered immune response damages the lining of your small intestine. It leads to inflammation and affects nutrient absorption. Homeopathy corrects this root cause of celiac disease. These medications help reduce inflammation and support gut healing. They reduce the severity, frequency, and relapses of celiac disease.
Top five homeopathic medicines for celiac disease
Lycopodium clavatum (Lyc.)
Common name: Club moss
Celiac disease with weak digestion calls for Lycopodium. The people needing this remedy feel bloated and full of gas with gastric distension. Even eating a little makes them feel full like gas is rolling. They complain of acidity with excessive flatulence.
Celiac disease with heaviness and sharp, persistent pain in the right upper part of the abdomen indicates Lycopodium. There can be a shooting type of pain across the lower abdomen along with marked burning and belching. Most gastric symptoms worsen in the evening and from fatty food.
Natrum sulphuricum (Nat-s.)
Common name: Sulfate of sodium
Natrum sulph. is indicated for celiac disease with diarrhea that is yellow, watery, voluminous with a greasy stool. In these cases, there is a burning sensation in the anus after passing stool. Rumbling and gurgling bowel sounds accompany diarrhea. Cramps are felt around the umbilical region. Abdominal pain is relieved by gently rubbing the belly.
Carbo vegetables (carb-v.)
Common name: Vegetable charcoal
Carbo veg. helps manage celiac disease with frequent and foul-smelling stools. There is an ineffectual urge to pass stool, accompanied by a lot of flatulence and burning in the abdomen. A distended abdomen makes wearing tight clothing around the waist difficult.
Cinchona officinalis – China (Chin.)
Common name: Peruvian bark
China helps in managing celiac disease with diarrhea and marked physical weakness. Yellow, frothy stool with excessive flatulence while passing stool may be noted. The stool often contains undigested food.
China yields good results in celiac disease, where the pain is due to gas. This pain is relieved by bending double. Bloated abdomen and belching with a bitter taste are other symptoms of this remedy.
Arsenic album (Ars. alb.)
Common name: Arsenious acid
Ars. alb. is a useful medicine for celiac disease with nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. It is suited for celiac disease with extreme weight loss and acute exhaustion. Exhaustion is due to profuse, watery stools mixed with mucus and undigested food. Diarrhea is often foul-smelling that gets worse after eating and at midnight.
Cramping, cutting, tearing, or burning pains in the intestines is present. There is a loss of appetite along with diarrhea. Other symptoms include constant nausea and green-yellow vomiting.
Causes for celiac disease
Celiac disease is an autoimmune response triggered by the consumption of gluten. Genetic predisposition is the key factor that increases the risk for celiac disease. HLA DQ2 and HLA DQ8 are the genes responsible for celiac disease.
Environmental factors play a role, like when gluten was introduced to you in infancy. Viral infections and changes in your gut microbes contribute to celiac disease.
The combination of genetics, environmental factors, and gut microbes leads to an abnormal immune response. This immune response causes inflammation and damages the lining of the small intestine.
Symptoms of celiac disease
Celiac disease symptoms can broadly be classified into gastric, iron-deficiency anemia, and malnutrition.
- Diarrhea
Diarrhea with loose and frequent bowels is a classic symptom of celiac disease. This results when your body attempts to expel irritants like gluten quickly.
- Abdominal pain
Pain in your abdomen in celiac disease results from inflammation in the small intestine. It can cause discomfort and tenderness.
- Bloating
You may feel bloated due to your gut’s inability to digest gluten. This leads to gas accumulation in your digestive system.
- Constipation
This is a common effect of gluten-induced inflammation in celiac disease. Your disrupted bowel motility can make you feel constipated.
- Steatorrhea
Fatty stools may occur due to undigested fats passing through your intestine and appearing in your stool.
Symptoms of iron-deficiency anemia include:
You may feel weakness and fatigue due to iron-deficiency anemia in celiac disease. This results from an insufficient supply of oxygen to your tissues. Other symptoms of anemia include,
- Pallor
A pale complexion is a visible sign of reduced hemoglobin levels.
- Cold hands
When you have anemia, your body prioritizes blood flow to vital organs. Your hands may feel cold due to decreased blood circulation.
- Koilonychia
Your nails get brittle or concave, indicating impaired nail bed blood supply due to iron deficiency.
- Headache
Headaches arise from the decreased oxygen supply to your brain. It contributes to neurological symptoms along with anemia.
- Mouth sores
You may develop mouth sores due to the effect of the anemia on your mucus membranes.
Symptoms of malnutrition include:
- Weight loss
Unintended weight loss in celiac disease can be due to nutrient malabsorption by damaged small intestine lining.
- Delayed growth
There can be growth delays and failure to thrive in children due to nutrient deficiencies.
- Muscle wasting
A low muscle tone can be a symptom due to inadequate absorption of essential muscle nutrients.
- Dental issues
Dental enamel defects, like pitting and translucent teeth, are common in celiac disease.
- Mood changes
Mood swings, irritability, and depression are linked to the neurological impact of celiac disease on the central nervous system.
- Menstrual irregularities
Irregular periods or infertility can result from hormonal imbalances linked to untreated celiac disease.
- Dermatitis herpetiformis
Gluten rash develops in about 15%-25% of people with celiac disease. Celiac rash looks like clusters of bumps or blisters that itch.
Treatment for celiac disease
The first step in celiac disease treatment is to stop eating gluten. You cannot change how your body reacts to gluten. However, you can prevent gluten-triggered reactions. Once you stop eating gluten, the lining of your small intestine begins to heal. Gradually, your intestines will absorb nutrients again. However, you need to follow a strict gluten-free diet throughout your life to prevent damaging your small intestine again. Additional treatments for celiac disease include nutritional supplements, medications, and steroids.
Diet and lifestyle modification for celiac disease
The diet itself is the first line of treatment for celiac disease. Strictly adhering to a gluten-free diet is essential to manage celiac disease. It includes avoiding wheat, barley, and rye.
Other diet and lifestyle considerations for celiac disease include:
- Switch to naturally gluten-free grains like rice, pearl millet, sorghum, quinoa, and corn.
- Look for gluten-free alternatives for your staples like bread, pasta, and snacks in stores.
- Before you buy processed foods and condiments, please read the labels carefully to identify hidden sources of gluten in them.
- To avoid cross-contamination in your kitchen, cook your gluten-free meals in separate utensils.
- Consume seasonal fresh fruits, local vegetables, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy for nutrient-rich options.
- Consult a dietitian to ensure good nutrition and monitor for possible deficiencies.
- Some medications, cosmetics, and supplements contain gluten. Read labels cautiously before buying them.
- Look for gluten-free dining options while eating outside.
Conclusion
Getting diagnosed with celiac disease can change your overall life. Homeopathy is a complementary mode of management for celiac disease. Constitutional homeopathic medicines for celiac disease can provide symptomatic relief and decrease the sensitivity of your gut.
References
- Definition & facts for celiac disease [Internet]. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. NIDDK – National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2022 [cited 2024 Jan 18]. Available from: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/celiac-disease/definition-facts
- Dieli-Crimi R, Cénit MC, Núñez C. The genetics of celiac disease: A comprehensive review of clinical implications. J Autoimmun [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2024 Jan 18];64:26–41. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26194613/
- Shivani W, Shivani -., Doda W. celiac Disease & Its Homoeopathic Management [Internet]. Tjhms.com. [cited 2024 Jan 18]. Available from:https://tjhms.com/uploadfiles/15.%20celiac%20Disease%20&%20Its%20Homoeopathic%20Management.20201030124904.pdf
- Martina S, Fabiola F, Federica G, Chiara B, Gioacchino L, Francesco DM, et al. Genetic susceptibilty and celiac disease: what role do HLA haplotypes play? Acta Bio Medica?: Atenei Parmensis [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2024 Jan 18];89(Suppl 9):17. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.23750/abm.v89i9-S.7953
- Aronsson CA, Lee H-S, Liu E, Uusitalo U, Hummel S, Yang J, et al. Age at gluten introduction and risk of celiac disease. Pediatrics [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2024 Jan 18];135(2):239–45. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2014-1787
- Olshan KL, Leonard MM, Serena G, Zomorrodi AR, Fasano A. Gut microbiota in celiac disease: microbes, metabolites, pathways and therapeutics. Expert Rev Clin Immunol [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2024 Jan 18];16(11):1075–92. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/1744666x.2021.1840354
- Alkhiari R. Psychiatric and neurological manifestations of celiac disease in adults. Cureus [Internet]. 2023 [cited 2024 Jan 18];15(3). Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.7759/cureus.35712
- Freeman HJ. Reproductive changes associated with celiac disease. World J Gastroenterol [Internet]. 2010 [cited 2024 Jan 18];16(46):5810. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i46.5810
- Caproni M, Bonciolini V, D’Errico A, Antiga E, Fabbri P. celiac disease and dermatologic manifestations: Many skin clue to unfold gluten-sensitive enteropathy. Gastroenterol Res Pract [Internet]. 2012 [cited 2024 Jan 18];2012:1–12. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2012/952753
- Treatment for celiac disease [Internet]. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. NIDDK – National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2023 [cited 2024 Jan 18]. Available from: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/celiac-disease/treatment
- Mirza HA, Gharbi A, Bhutta BS. Dermatitis Herpetiformis. StatPearls Publishing; 2023.Available from:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK493163/
- Abbas A, Shahab T, Sherwani RK, Alam S. Addition of a short course of prednisolone to a gluten-free diet vs. Gluten-free diet alone in recovery of celiac disease: A pilot randomized controlled trial. Cureus [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2024 Jan 18];10(1). Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.7759/cureus.2118
- Leffler DA, Edwards-George J, Dennis M, Schuppan D, Cook F, Franko DL, et al. Factors that influence adherence to a gluten-free diet in adults with celiac disease. Dig Dis Sci [Internet]. 2008 [cited 2024 Jan 18];53(6):1573–81. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10620-007-0055-3
- Rai S, Kaur A, Chopra CS. Gluten-free products for celiac susceptible people. Front Nutr [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2024 Jan 18];5. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2018.00116
- Lizano-Díez I, Mariño EL, Modamio P. Gluten in pharmaceutical products: a scoping review. Syst Rev [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2024 Jan 18];10(1). Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13643-021-01772-9