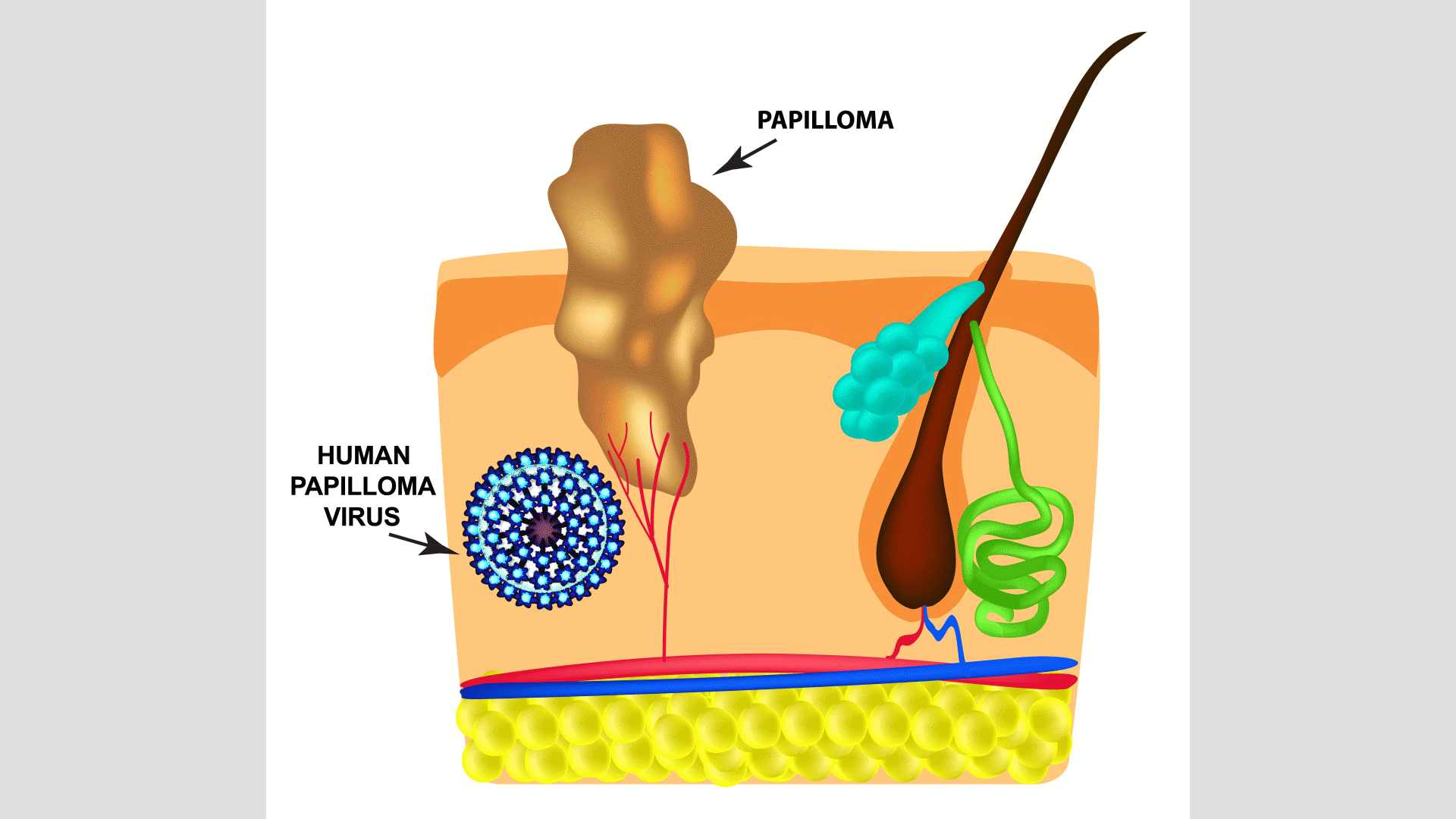
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a virus that can affect both men and women and is typically transmitted through skin-to-skin contact, often during sexual activity. HPV can cause warts on the skin or mucous membranes of the body, including the genitals, mouth, and throat. There are different strains of HPV, some of which can lead to more serious health issues. While many individuals with HPV may not show any symptoms and may not be aware of their infection, certain types of HPV can result in health problems like genital warts or cancer.
HPV can remain in the body for a long time without any visible signs, as the immune system usually fights off the virus. However, in some cases, HPV can persist and lead to complications later on. Fortunately, there are steps you can take to protect yourself from HPV. Homeopathic treatment for HPV focuses on enhancing the body’s natural healing abilities to combat the virus.
The most effective way to prevent HPV infection is through vaccination, which is safe and effective. If you are already infected with HPV, there are treatment options available to help manage the virus and reduce the risk of complications, allowing you to maintain good health.
Role of homeopathy in HPV
Homeopathy takes a comprehensive approach to addressing HPV by stimulating the body’s natural healing processes. While there is no cure for HPV, homeopathy focuses on managing symptoms and enhancing the immune system.
Six effective homeopathic medicines for HPV
Thuja occidentalis (Thuj.)
Common name: Cedar tree
Thuja is prescribed for HPV-related genital warts. It helps stimulate the body’s immune response to reduce the growth and recurrence of warts. Thuja is also indicated for treating skin conditions and addressing emotional symptoms such as anxiety and depression.
Calendula officinalis (Calen.)
Common name: Marigold
Calendula is known for its antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties. It is used topically in cream or ointment form to soothe irritated skin caused by genital warts. Calendula promotes healing and helps alleviate discomfort associated with HPV-related skin lesions. It also helps manage cervical lesions.
Nitricum acidum (Nit-Ac)
Common name: Nitric acid
Nitric acid is prescribed for genital warts with a tendency to bleed easily. It helps reduce pain, burning sensations, and discomfort associated with warts. Nitric acid is also indicated for addressing anxiety, irritability, and pessimism often experienced by individuals with HPV.
Medorrhinum (Med.)
Common name: Gonorrhoeal virus
Medorrhinum is used for treating stubborn genital warts. It is prescribed when warts are hard, large, and cauliflower-like in appearance. Medorrhinum helps boost the body’s immune response and addresses underlying susceptibility to recurrent infections.
Silicea (Sil.)
Common name: Silica
Silicea is indicated for individuals with weakened immune systems susceptible to recurrent HPV infections. It enhances the body’s defense mechanisms, making it more resilient against viral infections. Silicea also promotes the expulsion of toxins from the body, aiding in eliminating HPV-related symptoms such as warts.
Graphites (Graph.)
Common name: Black lead
Graphites is prescribed for HPV-related skin conditions characterized by moist, oozing eruptions, and cracked skin. It helps relieve itching and inflammation of the affected area, promoting healing and preventing secondary infections. Graphites is also indicated for individuals with a tendency towards obesity and sluggish metabolism, often seen in HPV cases.
Causative factors of HPV
-
Sexual contact
HPV is most commonly spread through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sexual acts. Multiple sexual partners can increase the risk of exposure to the virus.
-
Lack of condom use
Condoms provide some protection against HPV. Inconsistent or improper condom use can increase the risk of HPV transmission.
-
Weak immune system
A weak immune system due to various factors like illness, stress, or certain medicines can make it harder for the body to fight off HPV infections. Those with a compromised immune system, such as individuals with HIV or AIDS, are at higher risk of developing HPV-related complications.
-
Genital warts
Genital warts caused by certain strains of HPV can increase the risk of transmitting the virus to sexual partners.
-
Poor hygiene
Poor hygiene practices like not washing the genital area on a regular basis can increase the risk of HPV transmission. Keeping the genital area clean and practicing good personal hygiene will help reduce the risk of contracting HPV.
Symptoms of HPV
-
Genital warts
These are growths or bumps that appear on the genital area. They can be small or large, flat or raised, and sometimes clustered together, resembling a cauliflower.
-
Abnormal pap smear results
Abnormal cells in the cervix detected during a pap smear test may indicate HPV infection.
-
No symptoms at all
In many cases, HPV infection doesn’t cause any noticeable symptoms, especially in the early stages. In such cases, the virus can still be transmitted to others. Regular screenings and practicing safe sex are crucial for prevention and early detection.
Treatment for HPV
In conventional medicine, physicians may prescribe creams or gels to be applied directly to genital warts in order to eliminate them. If the warts are large or do not respond to creams, they may propose surgical removal, which could involve freezing, burning, or cutting them off. In more severe cases such as abnormal cells in the cervix, doctors may suggest procedures to remove them, and treatments like chemotherapy or radiation may be necessary for cancers caused by HPV.
Furthermore, there are vaccines accessible to prevent specific types of HPV, administered as shots to guard against genital warts and cervical cancer. In general, treatment is focused on alleviating symptoms, avoiding complications, and halting the spread of the virus, with healthcare providers collaborating with patients to determine the most suitable course of action based on their unique circumstances.
Lifestyle changes for managing HPV
-
Safe sex practice
Practicing safe sex by using condoms consistently and correctly will reduce the risk of contracting HPV. The number of sexual partners should be limited as it decreases the chances of exposure to the virus.
-
Regular screening
Regular screenings, such as pap smear for cervical cancer and HPV tests, are essential for early detection of HPV-related complications. Following recommended screening guidelines can help identify any abnormalities early on and allow early treatment.
-
Regular exercise
Engaging in regular physical activity might help maintain weight, reduce stress, and strengthen the immune system. Aim for at least 30 minutes of exercise most days of the week.
-
Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
Smoking weakens the immune system and increases the risk of developing HPV-related complications. Similarly, excessive alcohol consumption can impair immune function and overall health.
-
Stress
Chronic stress might weaken the immune system and increase susceptibility to infections. Finding some ways to manage stress, such as practicing relaxation techniques, mindfulness, or engaging in enjoyable activities, is important for overall well-being.
-
Maintaining good hygiene
Practicing good personal hygiene, like regular washing of hands and keeping the genital area clean, can reduce the risk of HPV transmission.
-
Vaccination
Vaccination against HPV is available and recommended for both males and females to prevent some strains of the virus. Following the recommended vaccination schedule can provide protection against HPV-related complications.
Conclusion
Regular screenings and vaccinations are effective in preventing HPV-related complications such as cervical cancer and genital warts. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, balanced diet, safe sexual practices, and avoiding smoking can further lower the risk of HPV transmission and associated illnesses. Homeopathic remedies can also help alleviate symptoms and promote overall well-being for those already affected by HPV. By staying informed, seeking medical advice, and advocating for preventive measures, individuals can tackle the challenges posed by HPV.
References
- Naresh A, Hagensee M, Myers L, Cameron J. Association of diet quality and dietary components with clinical resolution of HPV. Nutr Cancer [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2024 Feb 9];73(11–12):2579–88. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/01635581.2020.1841251
- STD Facts – Human papillomavirus (HPV) [Internet]. Cdc.gov. 2022 [cited 2024 Feb 9]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/std/hpv/stdfact-hpv.htm
- Dey S, Hashmi S, Saha S, Mandal M, Shaikh AR, Agrawal E, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, pilot trial of individualized homeopathic medicines for cutaneous warts. Homeopathy [Internet]. 2021; Available from: https://www.thieme-connect.com/products/ejournals/pdf/10.1055/s-0040-1722232.pdf
- Rana DDK, Villan DJ. Homoeopathic approach in the management of warts: A case report. Int J Homoeopathic Sci [Internet]. 2021;5(2):162–5. Available from: https://www.homoeopathicjournal.com/articles/378/5-1-106-146.pdf
- Jasmin K. M J, Fathima A A. A homoeopathic case report on Palmar warts treated with silicea. Int J Sci Res (Raipur) [Internet]. 2023;12(10):942–4. Available from: https://www.ijsr.net/archive/v12i10/SR231011154005.pdf
- Oza, Piyush Mahendra. (2016). Homeopathic management of warts. Indian Journal of Drugs in Dermatology. 2. 45. 10.4103/2455-3972.184085. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/304025985_Homeopathic_management_of_warts
- Mishra DN, Mishra R. WARTS & ITS HOMEOPATHIC REMDIES [Internet]. Jetir.org. [cited 2024 Feb 9]. Available from: https://www.jetir.org/papers/JETIR2207569.pdf
- Iljazovi? E, Ljuca D, Šahimpaši? A, Avdi? S. Efficacy in treatment of cervical HrHPV infection by combination of beta interferon, and herbal therapy in woman with different cervical lesions. Bosn J Basic Med Sci [Internet]. 2008 [cited 2024 Feb 9];6(4):79–84. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2006.3128