Introduction
6.7% of Indians struggle with tinnitus. 1 While it may only last a few days or weeks for some people, it may persist longer for others.
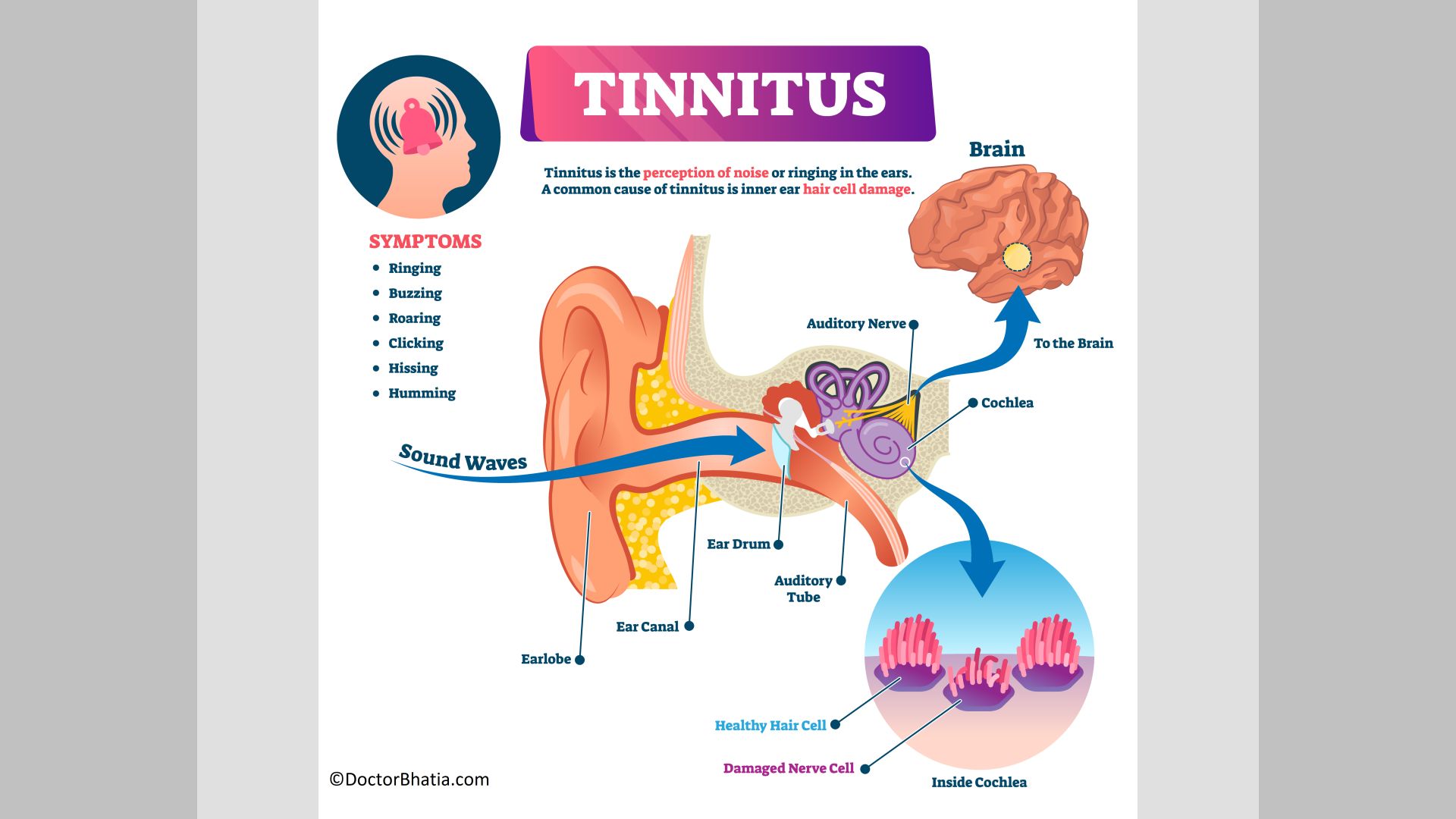
Tinnitus is the perception of sound when there is no actual external sound. It can be ringing, buzzing, hissing, whistling, or vibrating sounds in the ears and head.
This noise level might fluctuate in intensity and frequency. Tinnitus gets worse when the background noise is low. You might feel more sensitive to it at night when trying to sleep in a quiet place.
Tinnitus can affect a person’s quality of life as it can disrupt sleep, interfere with concentration, and result in emotional anguish.
Homeopathy can provide a good solution as there is no specific treatment for tinnitus. Homeopathic remedies are natural, safe, have no side effects, and have better results in the long run.
Role of homeopathic medicines in tinnitus
The natural and potentized homeopathic medications support your inherent healing ability to repair and restore normal ear function. Homeopathic medicines for tinnitus treatment address the disease’s symptoms and the anxiety that come with this condition. Thus, eliminating the disease from its roots in a very safe and gentle manner.
Top five homeopathic medicines for tinnitus
Homeopathic experts treat tinnitus with an individualized approach. Thus one medication will not cure all tinnitus cases. However, here are the top 5 homeopathic remedies for tinnitus.
Kalium muriaticum (Kali-m.)
Common name: Chloride of potassium
Kalium muriaticum is one of the best homeopathic medicines for tinnitus. This remedy is suited for tinnitus with excessive nasal buildup or mucus discharge in the nose or throat.
Kali. mur. works well for those with a history of long-standing ear discharges, also known as otorrhea. It treats tinnitus with popping and crackling noises in the ear. These noises get worse when swallowing. Other indications of this remedy include otitis media, deafness from ear catarrh, and swollen ear glands.
Natrum salicylicum (Nat-sal.)
Common name: Salicylate of sodium
Natrum salicylicum is the best homeopathic medicine for tinnitus with vertigo. This medicine is indicated to treat tinnitus developing due to meniere’s disease. This includes a triad of symptoms, noises in the ear, hearing loss, and vertigo.
Natrum salicylicum treats tinnitus with constant and low-tone sounds. It helps with tinnitus that gets worse on sitting up or rising from bed. Lying down gives relief from tinnitus. Other indications of this remedy include deafness and auditory vertigo.
Chenopodium anthelminticum (Chen-a.)
Common name: Jerusalem oak
Chenopodium anthelminticum is a very good homeopathic medicine for tinnitus with sudden spells of vertigo. This remedy helps in tinnitus, where the person can hear high-pitched sounds but is deaf to human sounds.
Chenopodium is the best remedy for tinnitus with buzzing, ringing, or roaring noises in the ear. Another characteristic symptom of this remedy is tinnitus synchronous with heartbeats.
Graphites naturalis
Common name: Black lead
A good homeopathic medicine for somatic tinnitus is Graphites naturalis.
This remedy helps with tinnitus with hissing and buzzing sounds. Sometimes, a person may also hear cracking sounds in the ears.
Graphites constitution is very sensitive to noise from passing vehicles. Every time the person moves his head and jaw, tinnitus symptoms worsen.
Other indications of Graphites include a feeling of stuffy, dryness in the ears, torpor of the auditory nerve, and aural vertigo.
Chininum sulphuricum (Chinin-s)
Common name: Sulfate of quinine
Tinnitus can be managed well with the homeopathic medicine, Chininum sulphuricum. This remedy is suited for ringing in the ears. There is violent ringing, buzzing, and roaring in the ears.
Vertigo and a decline in hearing also indicate the need for Chininum sulph.. This remedy works wonders in those people with headaches and meniere’s disease.
Causes of tinnitus
The most common cause of tinnitus is excessive and prolonged exposure to loud noises. 90% of people who have tinnitus experience some degree of hearing loss due to noise.3 The loud noises cause irreversible damage to the cochlea, an inner ear spiral shaped organ.
The other causes of tinnitus include:
Occupation
Occupation has a marked impact on developing tinnitus.3 People who operate with chainsaws, weapons, or other noisy equipment or frequently listen to loud music are among those whose profession puts them in danger of tinnitus. Other professions like pilots, rock musicians, street repair workers, and landscapers are at higher risk of tinnitus.
Blockages
Ear blockages caused by a wax buildup, an ear infection, or, rarely, a benign tumor on the auditory nerve can cause tinnitus.4
Medications
Tinnitus is a possible side effect for about several prescription and over-the-counter medicines. Some medications include antibiotics, anti-inflammatories, loop diuretics, and antidepressants.
Cochlear degeneration
The degeneration of the cochlea or other ear structures due to aging can lead to tinnitus.5
Meniere’s disease
The inner ear affected by meniere’s disease can cause tinnitus.6
Otosclerosis
The tiny bones of the middle ear stiffen due to otosclerosis, leading to tinnitus.7
Joint problems
Issues with the neck or jaw, such as temporomandibular joint (TMJ) syndrome, can cause tinnitus.8
Head and neck injuries
Chronic tinnitus can be due to head and neck injuries.9
Symptoms of tinnitus
The symptom of tinnitus is described as a ringing in the ears, although no external sound is present. The most common type is subjective tinnitus, which only you can hear. Tinnitus can be felt in one or both ears. The other symptoms include:
- The phantom noises like clicking, hissing, buzzing, and humming.
- Noise ranging in different pitches, it can be a low roar or a high screech.
- The tinnitus can be so loud that it makes it difficult to focus or hear outside noise.
- Constant ringing or fluctuant in nature.
- Tinnitus can sound like a pulsing or whooshing sound, often synchronized with your heartbeat. The term for this is pulsatile tinnitus or also called objective tinnitus. When examining, your doctor might be able to hear this type of tinnitus.
Treatment for tinnitus
The course of treatment for tinnitus depends on its cause.
- If a medicine is the cause, your doctor may advise stopping the prescription or switching to a different one.
- If it’s a health issue like blood pressure causing tinnitus, its treatment can help reduce tinnitus.
- If the cause is earwax, the doctor can gently remove the buildup.
Other therapeutic alternatives could be:
Hearing devices
These devices help with tinnitus and hearing loss brought on by aging. They increase the volume of the sounds you need to hear while masking the ringing.
Acoustic maskers
They are worn in or behind the ear. These continuously emit low-level white noise. This lessens ringing interference.
Retraining therapy
You get counseling and will be given a device that plays tonal music to cover up the ringing.
Relaxation
Stress might make your tinnitus worse. Working on techniques to reduce your anxiety, such as physical activity or deep breathing, can help reduce tinnitus.
Diet and lifestyle modifications for tinnitus
Eating nutrient-dense food will help your body heal itself and can even help ease your tinnitus symptoms.
Vitamin B12
When you have noise-induced tinnitus, vitamin B12-rich foods like salmon, poultry, meat, eggs, and mackerel can help you feel better.
Bromelain
Pineapple contains bromelain, a compound that can help relieve tinnitus symptoms by lowering the inflammation in your body.
Potassium
Foods high in potassium, such as apricots, sweet potatoes, pears, papayas, bananas, yogurt, spinach, mangos, and apples, may help you maintain a healthy fluid balance throughout the body.
Zinc
Low zinc levels can occasionally result in ringing in the ears. So ensure you eat enough nuts, dark chocolate, yogurt, chicken, steak, spinach, lamb, and shellfish to maintain your zinc levels.
Folate
Folate helps to relieve tinnitus, abrupt hearing loss, and age-related hearing loss by improving blood flow to the inner ear.
Conclusion
When you have tinnitus, you may constantly hear auditory phantom noises. There is no known conventional treatment that can cure tinnitus or lessen its effects.
Homeopathic medicines play a significant role in tinnitus treatment. Consulting a homeopathic physician before using it can give good and safe results.
References
- Aryal S, Sharma Y, Prabhu P. Prevalence of tinnitus and its characteristics among Indian adult population. Annals of Otology and Neurotology [Internet]. 2022;5(01):015–20. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-0043-1769889
- Mazurek B, Olze H, Haupt H, Szczepek AJ. The more the worse: The grade of noise-induced hearing loss associates with the severity of tinnitus. Int J Environ Res Public Health [Internet]. 2010 [cited 2023 Aug 30];7(8):3071–9. Available from:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2954569/
- Engdahl B, Krog NH, Kvestad E, Hoffman HJ, Tambs K. Occupation and the risk of bothersome tinnitus: results from a prospective cohort study (HUNT). BMJ Open [Internet]. 2012 [cited 2023 Aug 25];2(1):e000512. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2011-000512
- Chan HBY, Low D, Yuen HW, How CH. Tinnitus – ringing in the ears. Singapore Med J [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2023 Aug 30];61(9):448–52. Available from:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7927175/
- Henry JA, Roberts LE, Caspary DM, Theodoroff SM, Salvi RJ. Underlying mechanisms of tinnitus: Review and clinical implications. J Am Acad Audiol [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2023 Aug 25];25(01):005–22. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.3766/jaaa.25.1.2
- Koenen L, Andaloro C. Meniere Disease. StatPearls Publishing; 2023.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK536955/ - Lima AF, Moreira FC, Costa IE, Azevedo C, Mar F, Dias L. Tinnitus and otosclerosis: An exploratory study about the prevalence, features and impact in daily life. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2023 Aug 25];26(03):e390–5. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-0041-1739967
- Edvall NK, Gunan E, Genitsaridi E, Lazar A, Mehraei G, Billing M, et al. Impact of temporomandibular joint complaints on tinnitus-related distress. Front Neurosci [Internet]. 2019 [cited 2023 Aug 25];13. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.00879
- Folmer RL, Griest SE. Chronic tinnitus resulting from head or neck injuries. Laryngoscope [Internet]. 2003 [cited 2023 Aug 25];113(5):821–7. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12792317
- Tinnitus [Internet]. NIDCD. [cited 2023 Aug 25]. Available from: https://www.nidcd.nih.gov/health/tinnitus
- Stahl G, Bagot J-L. Annals of Otolaryngology and Rhinology [Internet]. Jscimedcentral.com. 2022 [cited 2023 Aug 30]. Available from: https://www.jscimedcentral.com/public/assets/articles/otolaryngology-9-1287.pdf
- No title [Internet]. Nih.gov. [cited 2023 Aug 30]. Available from: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/fda/fdaDrugXsl.cfm?setid=dedd88fd-9bbf-4dc2-9f59-ba8ccce0b1be<
- Department of surgery [Internet]. Nyu.edu. [cited 2023 Aug 30]. Available from: https://froemkelab.med.nyu.edu/surgery/content?ChunkIID=38343