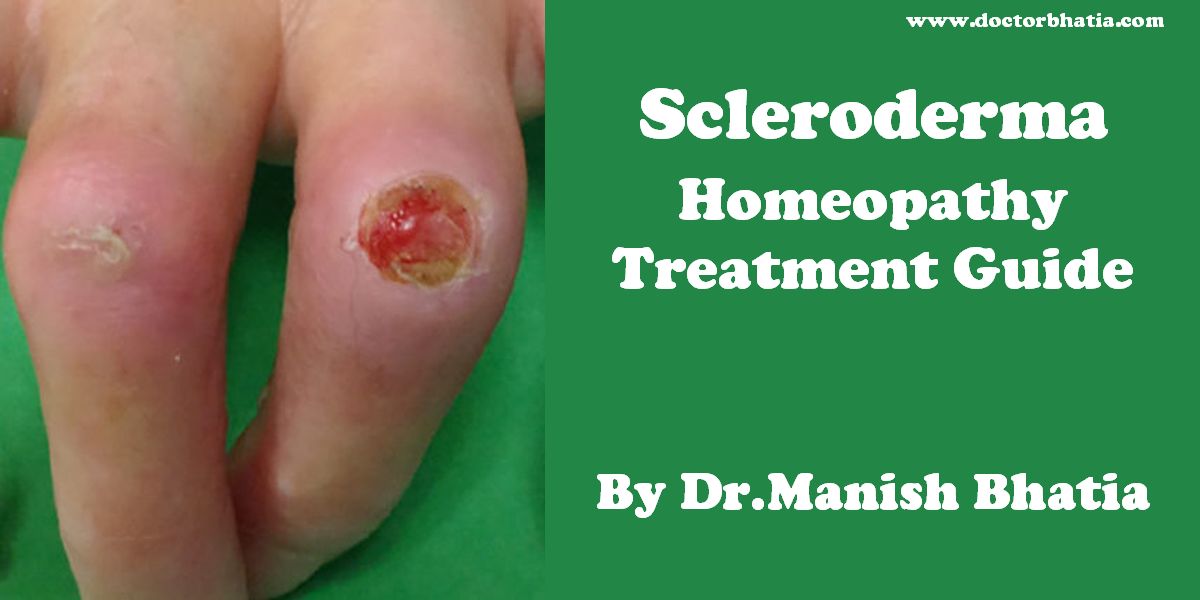
Scleroderma is a chronic disease characterized by excessive deposits of collagen in the skin or other organs. The localized type of the disease, while disabling, tends not to be fatal. The systemic type or systemic sclerosis, the generalized type of the disease, can be fatal as a result of heart, kidney, lung or intestinal damage autoimmune disease.[1]
Signs and symptoms of Scleroderma
Skin symptoms
Scleroderma affects the skin, and in more serious cases it can affect the blood vessels and internal organs. The most evident symptom is usually the hardening of the skin and associated scarring. The skin may appear tight, reddish or scaly. Blood vessels may also be more visible. Where large areas are affected, fat and muscle wastage may weaken limbs and affect appearance.
The seriousness of the disease varies hugely between cases. The two most important factors to consider are the level of internal involvement (beneath the skin) and the total area covered by the disease. In general, the more skin that is involved, the more severe the case of scleroderma.
For the systemic form of the disease, almost all patients (over 80%) have vascular symptoms and Raynaud’s phenomenon. During an attack, there is discoloration of the hands and feet in response to cold. Raynaud’s normally affects the fingers and toes.
Systemic scleroderma and Raynaud’s can cause painful ulcers on the fingers or toes which are known as digital ulcers.
Calcinosis is also common in systemic scleroderma, and is often seen near the elbows, knees or other joints.
Other organs
Diffuse scleroderma can cause musculoskeletal, pulmonary, gastrointestinal, renal and other complications.[1]Patients with larger amounts of cutaneous involvement are more likely to have involvement of the internal tissues and organs.
- Musculoskeletal
The first joint symptoms that patients with scleroderma have are typically non specific joint pains, which can lead to arthritis, or cause discomfort in tendons or muscles.[1] Joint mobility, especially of the small joints of the hand, may be restricted by calcinosis or skin thickening.[2] Patients may develop muscle weakness, or myopathy, either from the disease, or its treatments.[3]
- Lungs
Some impairment in lung function is almost universally seen in patients with diffuse scleroderma on pulmonary function testing;[4] however, it does not necessarily cause symptoms, such as shortness of breath. Some patients can develop pulmonary hypertension, or elevation in the pressures of the pulmonary arteries. This can be progressive, and lead to right sided heart failure. The earliest manifestation of this may be a decreased diffusion capacity on pulmonary function testing.
Other pulmonary complications in more advanced disease include aspiration pneumonia, pulmonary hemorrhage and pneumothorax.[1]
- Digestive tract
Endoscopic image of peptic stricture, or narrowing of the esophagus near the junction with the stomach due to chronic gastroesophageal reflux. This is the most common cause of dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing, in scleroderma.
Diffuse scleroderma can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract.[5] The most common manifestation in the esophagus is reflux esophagitis, which may be complicated by peptic stricturing, or benign narrowing of the esophagus.[6] This is best initially treated with proton pump inhibitors for acid suppression,[7] but may require bougie dilatation in the case of stricture.[5]
Scleroderma can decrease motility anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract.[5] The most common source of decreased motility involvement is the esophagus and the lower esophageal sphincter, leading to dysphagia and chest pain. As Scleroderma progresses, esophageal involvement from abnormalities in decreased motility may worsen due to progressive fibrosis (scarring). If this is left untreated, acid from the stomach can back up into the esophagus causing esophagitis, and GERD. Further scarring from acid damage to the lower esophagus many times leads to the development of fibrotic narrowing, also known as strictures which can be treated by dilitation, and Barrett’s esophagus. The small intestine can also become involved, leading to bacterial overgrowth and malabsorption, of bile salts, fats, carbohydrates, proteins, and vitamins. The colon can be involved, and can cause pseudo-obstruction or ischemic colitis.[1]
Rarer complications include pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis, or gas pockets in the bowel wall, wide mouthed diverticula in the colon and esophagus, and liver fibrosis. Patients with severe gastrointestinal involvement can become profoundly malnourished.[6]
Scleroderma may also be associated with gastric antral vascular ectasia (GAVE), also known as watermelon stomach. This is a condition where atypical blood vessels proliferate usually in a radially symmetric pattern around the pylorus of the stomach. GAVE can be a cause of upper gastrointestinal bleeding or iron deficiency anemia in patients with scleroderma.[6]
- Kidneys
Renal involvement, in scleroderma, is considered a poor prognostic factor and not infrequently a cause of death in patients with scleroderma.[8]
The most important clinical complication of scleroderma involving the kidney is scleroderma renal crisis. Symptoms of scleroderma renal crisis are malignant hypertension (high blood pressure with evidence of acute organ damage), hyperreninemia (high renin levels), azotemia (kidney failure with accumulation of waste products in the blood) and microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (destruction of red blood cells).[9] Apart from the high blood pressure, hematuria (blood in the urine) and proteinuria (protein loss in the urine) may be indicative.[10]
In the past scleroderma renal crisis was almost uniformily fatal.[11] While outcomes have improved significantly with the use of ACE inhibitors[12][13] the prognosis is often guarded, as a significant number of patients are refractory to treatment and develop renal failure. Approximately 5-10% of all scleroderma patients develop renal crisis at some point in the course of their disease.[14] Patients that have rapid skin involvement have the highest risk of renal complications.[14] It is most common in diffuse cutaneous scleroderma, and is often associated with antibodies against RNA polymerase (in 59% of cases). Many proceed to dialysis, although this can be stopped within three years in about a third of cases. Higher age and (paradoxically) a lower blood pressure at presentation make it more likely that dialysis is needed.[15]
Treatments for scleroderma renal crisis include ACE inhibitors, which are also used for prophylaxis,[14][13] and renal transplantation. Transplanted kidneys are known to be affected by scleroderma and patients with early onset renal disease (within one year of the scleroderma diagnosis) are thought to have the highest risk for recurrence.[16]
Diagnosis for Scleroderma
Diagnosis is by clinical suspicion, presence of autoantibodies (specifically anti-centromere and anti-scl70/anti-topoisomerase antibodies) and occasionally by biopsy. Of the antibodies, 90% have a detectable anti-nuclear antibody. Anti-centromere antibody is more common in the limited form (80-90%) than in the systemic form (10%), and anti-scl70 is more common in the diffuse form (30-40%) and in African-American patients (who are more susceptible to the systemic form).[17]
In 1980 the American College of Rheumatology agreed upon diagnostic criteria for scleroderma.[18]
Types of Scleroderma
There are three major forms of scleroderma: diffuse, limited (CREST syndrome) and morphea/linear. Diffuse and limited scleroderma are both a systemic disease, whereas the linear/morphea form is localized to the skin. (Some physicians consider CREST and limited scleroderma one and the same, others treat them as two separate forms of scleroderma.) There is also a subset of the systemic form known as “systemic scleroderma sine scleroderma”, meaning the usual skin involvement is not present.
Diffuse scleroderma
Diffuse scleroderma (progressive systemic sclerosis) is the most severe form – it has a rapid onset, involves more widespread skin hardening, will generally cause much internal organ damage (specifically the lungs and gastrointestinal tract), and is generally more life threatening.
Limited scleroderma/CREST syndrome
The limited form is much milder: it has a slow onset and progression, skin hardening is usually confined to the hands and face, internal organ involvement is less severe, and a much better prognosis is expected.
Sclerotic piece-meal necrosis of the tip of the thumb in a patient with scleroderma.
In typical cases of limited scleroderma, Raynaud’s phenomenon may precede scleroderma by several years. Raynaud’s phenomenon is due to vasoconstriction of the small arteries of exposed peripheries – particularly the hands and feet – in the cold. It is classically characterised by a triphasic colour change – first white, then blue and finally red on rewarming. The scleroderma may be limited to the fingers – known as sclerodactyly.
The limited form is often referred to as CREST syndrome.[19] “CREST” is an acronym for the five main features:
- Calcinosis
- Raynaud’s syndrome
- Esophageal dysmotility
- Sclerodactyly
- Telangiectasia
CREST is a limited form associated with antibodies against centromeres and usually spares the lungs and kidneys.
Morphea/linear scleroderma
Morphea/linear scleroderma involves isolated patches of hardened skin – there generally is no internal organ involvement.[20]
Causes of Scleroderma
There is no clear obvious cause for scleroderma and systemic sclerosis. Genetic predisposition appears to be limited: genetic concordance is small; still, there often is a familial predisposition for autoimmune disease. Polymorphisms in COL1A2 and TGF-?1 may influence severity and development of the disease. There is limited evidence implicating cytomegalovirus (CMV) as the original epitope of the immune reaction, and organic solvents and other chemical agents have been linked with scleroderma.[17]
One of the suspected mechanisms behind the autoimmune phenomenon is the existence of microchimerism, i.e. fetal cells circulating in maternal blood, triggering an immune reaction to what is perceived as “foreign” material.[21][17]
A distinct form of scleroderma and systemic sclerosis may develop in patients with chronic renal failure. This entity, nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy or nephrogenic systemic fibrosis,[22] has been linked to the exposure to gadolinium-containing radiocontrast.[23]
Bleomycin[24] (a chemotherapeutic agent) and possibly taxane chemotherapy[25] may cause scleroderma, and occupational exposure to solvents has been linked with an increased risk of systemic sclerosis.[26]
Pathophysiology
The overproduction of collagen is thought to result from an autoimmune dysfunction, in which the immune system would start to attack the kinetochore of the chromosomes. This would lead to genetic malfunction of nearby genes. T cells accumulate in the skin; these are thought to secrete cytokines and other proteins that stimulate collagen deposition. Stimulation of the fibroblast, in particular, seems to be crucial to the disease process, and studies have converged on the potential factors that produce this effect.[17]
A significant player in the process is transforming growth factor (TGF?). This protein appears to be overproduced, and the fibroblast (possibly in response to other stimuli) also overexpresses the receptor for this mediator. An intracellular pathway (consisting of SMAD2/SMAD3, SMAD4 and the inhibitor SMAD7) is responsible for the secondary messenger system that induces transcription of the proteins and enzymes responsible for collagen deposition. Sp1 is a transcription factor most closely studied in this context. Apart from TGF?, connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) has a possible role.[17] Indeed, a common CTGF gene polymorphism is present at an increased rate in systemic sclerosis.[27]
Damage to endothelium is an early abnormality in the development of scleroderma, and this too seems to be due to collagen accumulation by fibroblasts, although direct alterations by cytokines, platelet adhesion and a type II hypersensitivity reaction have similarly been implicated. Increased endothelin and decreased vasodilation has been documented.[17]
Jimenez & Derk[17] describe three theories about the development of scleroderma:
- The abnormalities are primarily due to a physical agent, and all other changes are secondary or reactive to this direct insult.
- The initial event is fetomaternal cell transfer causing microchimerism, with a second summative cause (e.g. environmental) leading to the actual development of the disease.
- Physical causes lead to phenotypic alterations in susceptible cells (e.g. due to genetic makeup), which then effectuate DNA changes which alter the cell’s behavior.
Therapy
There is no cure for every patient with scleroderma, though there is treatment for some of the symptoms, including drugs that soften the skin and reduce inflammation. Some patients may benefit from exposure to heat.[28]
Topical/symptomatic
Topical treatment for the skin changes of scleroderma do not alter the disease course, but may improve pain and ulceration. A range of NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) can be used to ease painful symptoms, such as naproxen. There is limited benefit from steroids such as prednisone. Episodes of Raynaud’s phenomenon sometimes respond to nifedipine or other calcium channel blockers; severe digital ulceration may respond to prostacyclin analogue iloprost, and the dual endothelin-receptor antagonist bosentan may be beneficial for Raynaud’s phenomenon.[29] The skin tightness may be treated systemically with methotrexate and cyclosporin.[29]
Kidney disease
Scleroderma renal crisis, the occurrence of acute renal failure and malignant hypertension (very high blood pressure with evidence of organ damage) in people with scleroderma, is effectively treated with drugs from the class of the ACE inhibitors. The benefit of ACE inhibitors extends even to those who have to commence dialysis to treat their kidney disease, and may give sufficient benefit to allow the discontinuation of renal replacement therapy.[29]
Lung disease and pulmonary hypertension
Active alveolitis is often treated with pulses of cyclophosphamide, often together with a small dose of steroids. The benefit of this intervention is modest.[30][31]
Pulmonary hypertension may be treated with epoprostenol, bosentan and possibly aerolized iloprost.[29]
Experimental treatments
Given the difficulty in treating scleroderma, treatments with a smaller evidence base are often tried to control the disease. These include antithymocyte globulin and mycophenolate mofetil; some reports have reported improvements in the skin symptoms as well as delaying the progress of systemic disease, but neither of them have been subjected to large clinical trials.[29]
While still experimental (given its high rate of complications), hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is being studied in patients with severe systemic sclerosis; improvement in life expectancy and severity of skin changes has been noted.[32]
Epidemiology
Scleroderma affects approximately 300,000 people in the United States. It is four times as common in women than in men. Incidence rates are estimated at 2-20 per million per year in the United States.
Juvenile scleroderma affects approximately 7000 children in the United States. The most common form of juvenile scleroderma is localized scleroderma, morphea and/or linear.
Advocacy
The Juvenile Scleroderma Network is an organization dedicated to provide emotional support and educational information to parents and their children living with juvenile scleroderma, to support pediatric research to identify the cause of and the cure for juvenile sscleroderma, and to enhance public awareness.[33]
In the US, the Scleroderma Foundation is a leading organization dedicated to raising awareness of the disease and assisting those who are affected.[34] The Scleroderma Research Foundation sponsors research into the condition.[35] Comedian and television presenter Bob Saget, a board member of the SRF, directed the 1996 ABC TV movie For Hope, starring Dana Delany, which depicts a young woman fatally affected by scleroderma; the film was based on the experiences of Saget’s sister Gay.[36]
Homeopathy Treatment for Scleroderma
Keywords: homeopathy, homeopathic, treatment, cure, remedy, remedies, medicine
Homeopathy treats the person as a whole. It means that homeopathic treatment focuses on the patient as a person, as well as his pathological condition. The homeopathic medicines are selected after a full individualizing examination and case-analysis, which includes the medical history of the patient, physical and mental constitution, family history, presenting symptoms, underlying pathology, possible causative factors etc. A miasmatic tendency (predisposition/susceptibility) is also often taken into account for the treatment of chronic conditions. A homeopathy doctor tries to treat more than just the presenting symptoms. The focus is usually on what caused the disease condition? Why ‘this patient’ is sick ‘this way’. The disease diagnosis is important but in homeopathy, the cause of disease is not just probed to the level of bacteria and viruses. Other factors like mental, emotional and physical stress that could predispose a person to illness are also looked for. No a days, even modern medicine also considers a large number of diseases as psychosomatic. The correct homeopathy remedy tries to correct this disease predisposition. The focus is not on curing the disease but to cure the person who is sick, to restore the health. If a disease pathology is not very advanced, homeopathy remedies do give a hope for cure but even in incurable cases, the quality of life can be greatly improved with homeopathic medicines.
The homeopathic remedies (medicines) given below indicate the therapeutic affinity but this is not a complete and definite guide to the homeopathy treatment of this condition. The symptoms listed against each homeopathic remedy may not be directly related to this disease because in homeopathy general symptoms and constitutional indications are also taken into account for selecting a remedy. To study any of the following remedies in more detail, please visit the Materia Medica section at Hpathy.
None of these medicines should be taken without professional advice and guidance.
Homeopathy Remedies for Scleroderma :
Alum., ant-c., arg-n., berb-a., bry., calc., caust., crot-t., echi., graph., hydrc., lyc., petr., phos., ran-b., rhus-r., sars., sil., still., sulph., thiosin., thyr.
References
- ^ a b c d e Klippel J (ed). Systemic sclerosis and related syndromes. Primer on the rheumatic diseases, 11th edition. The Arthritis Society. 1997;269. ISBN 1-91242-316-2.
- ^ Valentini G, Black C (2002). “Systemic sclerosis”. Best practice & research. Clinical rheumatology 16 (5): 807–16. doi:. PMID 12473275.
- ^ Olsen NJ, King LE, Park JH (1996). “Muscle abnormalities in scleroderma”. Rheum. Dis. Clin. North Am. 22 (4): 783–96. doi:. PMID 8923596.
- ^ Steen VD (2005). “The lung in systemic sclerosis”. Journal of clinical rheumatology 11 (1): 40–6. PMID 16357695.
- ^ a b c Sallam H, McNearney TA, Chen JD (2006). “Systematic review: pathophysiology and management of gastrointestinal dysmotility in systemic sclerosis (scleroderma)”. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 23 (6): 691–712. doi:. PMID 16556171.
- ^ a b c Rose S, Young MA, Reynolds JC (1998). “Gastrointestinal manifestations of scleroderma”. Gastroenterol. Clin. North Am. 27 (3): 563–94. doi:. PMID 9891698.
- ^ Hendel L, Hage E, Hendel J, Stentoft P (1992). “Omeprazole in the long-term treatment of severe gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in patients with systemic sclerosis”. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 6 (5): 565–77. PMID 1420748.
- ^ Ruangjutipopan S, Kasitanon N, Louthrenoo W, Sukitawut W, Wichainun R (2002). “Causes of death and poor survival prognostic factors in thai patients with systemic sclerosis”. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand 85 (11): 1204–9. PMID 12546318.
- ^ Steen VD, Mayes MD, Merkel PA (2003). “Assessment of kidney involvement”. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 21 (3 Suppl 29): S29–31. PMID 12889219.
- ^ Steen VD (1994). “Renal involvement in systemic sclerosis”. Clin. Dermatol. 12 (2): 253–8. doi:. PMID 8076263.
- ^ Steen VD (2003). “Scleroderma renal crisis”. Rheum. Dis. Clin. North Am. 29 (2): 315–33. doi:. PMID 12841297.
- ^ Rhew EY, Barr WG (2004). “Scleroderma renal crisis: new insights and developments”. Current rheumatology reports 6 (2): 129–36. doi:. PMID 15016343.
- ^ a b Steen VD, Medsger TA (2000). “Long-term outcomes of scleroderma renal crisis”. Ann. Intern. Med. 133 (8): 600–3. PMID 11033587.
- ^ a b c Jimenez S, Koenig AS. Scleroderma. eMedicine.com. Accessed: May 22, 2006.
- ^ Penn H, Howie AJ, Kingdon EJ, et al (August 2007). “Scleroderma renal crisis: patient characteristics and long-term outcomes“. QJM 100 (8): 485–94. doi:. PMID 17601770.
- ^ Pham PT, Pham PC, Danovitch GM, et al (October 2005). “Predictors and risk factors for recurrent scleroderma renal crisis in the kidney allograft: case report and review of the literature“. Am. J. Transplant. 5 (10): 2565–9. doi:. PMID 16162209.
- ^ a b c d e f g Jimenez SA, Derk CT (2004). “Following the molecular pathways toward an understanding of the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis”. Ann. Intern. Med. 140 (1): 37–50. PMID 14706971.
- ^ “Preliminary criteria for the classification of systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Subcommittee for scleroderma criteria of the American Rheumatism Association Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee” (1980). Arthritis Rheum. 23 (5): 581–90. PMID 7378088. Available online at “1980 Criteria for the Classification of Systemic Sclerosis“. Retrieved on 2007-08-05.
- ^ Winterbauer RH (1964). “Multiple telangiectasia, Raynaud’S phenomenon, sclerodactyly, and subcutanious calcinosis: a syndrome mimicking hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia”. Bulletin of the Johns Hopkins Hospital 114: 361–83. PMID 14171636.
- ^ Morpea CNN.com, (May 05, 2006).
- ^ Bianchi DW (2000). “Fetomaternal cell trafficking: a new cause of disease?”. Am. J. Med. Genet. 91 (1): 22–8. doi:. PMID 10751084.
- ^ Galan A, Cowper SE, Bucala R (2006). “Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy)”. Current opinion in rheumatology 18 (6): 614–7. doi:. PMID 17053507.
- ^ Boyd AS, Zic JA, Abraham JL (2007). “Gadolinium deposition in nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy”. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 56 (1): 27–30. doi:. PMID 17109993.
- ^ Sharma SK, Handa R, Sood R, et al (2004). “Bleomycin-induced scleroderma”. The Journal of the Association of Physicians of India 52: 76–7. PMID 15633728.
- ^ Farrant PB, Mortimer PS, Gore M (2004). “Scleroderma and the taxanes. Is there really a link?”. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 29 (4): 360–2. doi:. PMID 15245529.
- ^ Kettaneh A, Al Moufti O, Tiev KP, et al (2007). “Occupational exposure to solvents and gender-related risk of systemic sclerosis: a metaanalysis of case-control studies”. J. Rheumatol. 34 (1): 97–103. PMID 17117485.
- ^ Fonseca C, Lindahl GE, Ponticos M, et al (September 2007). “A polymorphism in the CTGF promoter region associated with systemic sclerosis“. N. Engl. J. Med. 357 (12): 1210–20. doi:. PMID 17881752.
- ^ Oliver GF, Winkelmann RK (1989). “The current treatment of scleroderma”. Drugs 37 (1): 87–96. PMID 2651089.
- ^ a b c d e Zandman-Goddard G, Tweezer-Zaks N, Shoenfeld Y (2005). “New therapeutic strategies for systemic sclerosis–a critical analysis of the literature”. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 12 (3): 165–73. PMID 16295521. Full text at PMC: 2275417
- ^ Tashkin DP, Elashoff R, Clements PJ, et al (June 2006). “Cyclophosphamide versus placebo in scleroderma lung disease“. N. Engl. J. Med. 354 (25): 2655–66. doi:. PMID 16790698.
- ^ Hoyles RK, Ellis RW, Wellsbury J, et al (December 2006). “A multicenter, prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of corticosteroids and intravenous cyclophosphamide followed by oral azathioprine for the treatment of pulmonary fibrosis in scleroderma“. Arthritis Rheum. 54 (12): 3962–70. doi:. PMID 17133610.
- ^ Nash RA, McSweeney PA, Crofford LJ, et al (2007). “High-dose immunosuppressive therapy and autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation for severe systemic sclerosis: long-term follow-up of the U.S. multicenter pilot study”. Blood 110 (4): 1388–96. doi:. PMID 17452515.
- ^ “Juvenile Scleroderma Network“. Retrieved on 2008-05-11.
- ^ “Scleroderma Foundation“. Retrieved on 2008-05-11.
- ^ “Scleroderma Research Foundation“. Retrieved on 2008-05-11..
- ^ Scleroderma at the Internet Movie Database