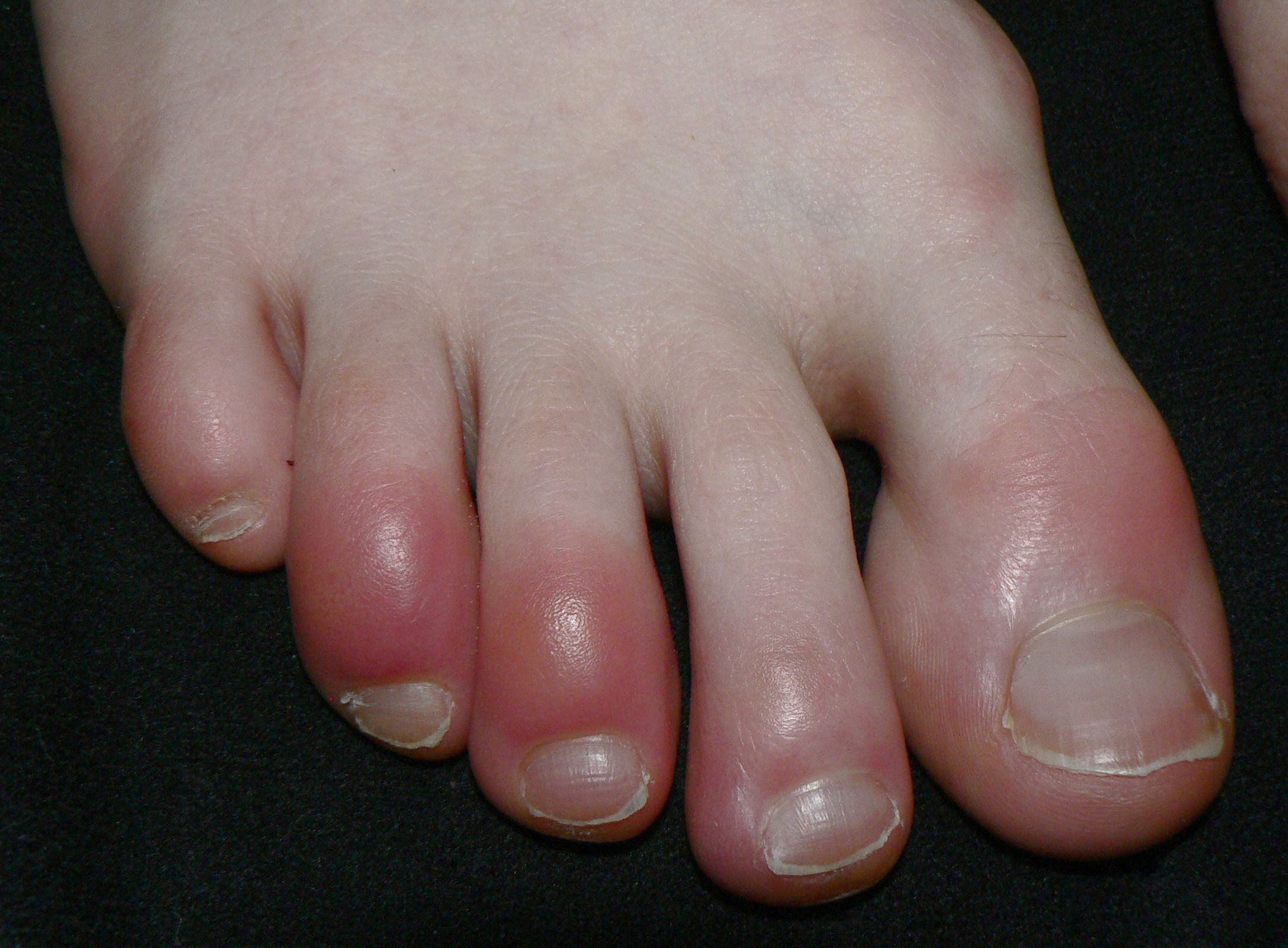
Chilblains, also called perniosis or blain, when occurring on the feet, is a medical condition that is often confused with frostbite and trench foot. Chilblains are acral ulcers that occur when a predisposed individual is exposed to cold and humidity. Acral refers to the extremities (e.g. fingers and toes). Chilblains are often idiopathic in origin but can be manifestations of serious medical conditions that need to be investigated. Chilblains can be prevented by keeping the feet and hands warm in cold weather. Smoking cessation and consultation with a dermatologist is advised.
Symptoms of Chilblain
- Ulceration of the digits and toes
- Itchy skin inflammation
- Skin redness
- Toe skin inflammation
- Finger skin inflammation
- Earlobe inflammation
Duration
With treatment, chilblains usually heal within 4 weeks
Treatments of Chilblain
- Keep area warm
- Avoid scratching
- Anti-itch creams, such as Calamine lotion
- Zambuk ointment
- Nifedipine may be used in more severe or recurrent cases.[1] Its vasodilation helps reduce pain, facilitate healing and prevent recurrences.[2]
- Diltiazem, a newer calcium channel blocker, may also be used.[3]
Prevention for Chilblain
Exposure:
- Avoid rapid changes in temperature.
- Wear gloves
- Use warm footwear.
- Keep hands and feet warm.
Dietary:
- Healthy diet
- Exercise
- High doses of vitamin K
Keep feet warm & dry! also take painkillers, and avoid alcohol before going out in snow
Homeopathy Treatment for Chilblain
Keywords: homeopathy, homeopathic, treatment, cure, remedy, remedies, medicine
Homeopathy treats the person as a whole. It means that homeopathic treatment focuses on the patient as a person, as well as his pathological condition. The homeopathic medicines are selected after a full individualizing examination and case-analysis, which includes the medical history of the patient, physical and mental constitution, family history, presenting symptoms, underlying pathology, possible causative factors etc. A miasmatic tendency (predisposition/susceptibility) is also often taken into account for the treatment of chronic conditions. A homeopathy doctor tries to treat more than just the presenting symptoms. The focus is usually on what caused the disease condition? Why ‘this patient’ is sick ‘this way’. The disease diagnosis is important but in homeopathy, the cause of disease is not just probed to the level of bacteria and viruses. Other factors like mental, emotional and physical stress that could predispose a person to illness are also looked for. No a days, even modern medicine also considers a large number of diseases as psychosomatic. The correct homeopathy remedy tries to correct this disease predisposition. The focus is not on curing the disease but to cure the person who is sick, to restore the health. If a disease pathology is not very advanced, homeopathy remedies do give a hope for cure but even in incurable cases, the quality of life can be greatly improved with homeopathic medicines.
The homeopathic remedies (medicines) given below indicate the therapeutic affinity but this is not a complete and definite guide to the homeopathy treatment of this condition. The symptoms listed against each homeopathic remedy may not be directly related to this disease because in homeopathy general symptoms and constitutional indications are also taken into account for selecting a remedy. To study any of the following remedies in more detail, please visit the Materia Medica section at Hpathy.
None of these medicines should be taken without professional advice and guidance.
Homeopathy Remedies for Chilblain :
Agar., all-c., aloe., alum., alumn., arn., ars., aur., bad., bell., bor., bufo., cadm-s., carb-an., carb-v., cham., chin., cop., croc., cycl., hyos., kali-ar., kali-c., kali-chl., kalm., lyc., mur-ac., nit-ac., nux-v., petr., ph-ac., phos., plan., puls., rhus-t., sep., stann., staph., sulph., sul-ac., thuj., zinc.
Footnotes
- ^ Rustin M, Newton J, Smith N, Dowd P (1989). “The treatment of chilblains with nifedipine: the results of a pilot study, a double-blind placebo-controlled randomized study and a long-term open trial”. Br J Dermatol 120 (2): 267–75. PMID 2647123.
- ^ Simon T, Soep J, Hollister J (2005). “Pernio in pediatrics“. Pediatrics 116 (3): e472–5. doi:. PMID 16140694.
- ^ Patra AK, Das AL, Ramadasan P. (2003). “Diltiazem vs. nifedipine in chilblains: A clinical trial“. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 69: 209–11. PMID : 17642888.